Cholangiography and interventional biliary radiology in adult liver transplantation
- PMID: 3880623
- PMCID: PMC3008426
- DOI: 10.2214/ajr.144.1.127
Cholangiography and interventional biliary radiology in adult liver transplantation
Abstract
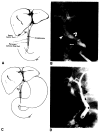
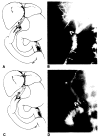
Radiographic assessment of the biliary tract is often essential in patients who have undergone liver transplantation. T- or straight-tube cholangiography, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiography all may be used. A total of 264 cholangiograms in 79 adult liver transplant patients (96 transplants) was reviewed. Normal radiographic features of biliary reconstructive procedures, including choledochocholedochostomy and choledochojejunostomy, are demonstrated. Complications diagnosed by cholangiography included obstruction, bile leaks, and tube problems, seen in eight, 24, and 12 transplants respectively. Stretching and incomplete filling of intrahepatic biliary ducts were frequently noted and may be associated with rejection and other conditions. Transhepatic biliary drainage, balloon catheter dilatation of strictures, replacement of dislodged T-tubes, and restoring patency of obstructed T-tubes using interventional radiologic techniques were important in avoiding complications and additional surgery in selected patients.
Figures
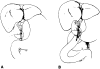
References
-
- Starzl TE. Liver transplantation. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1978;143:73–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

