PMMA dialyzers modulate both humoral and cell-mediate immune response to anti-COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) in a cohort of chronic hemodialyzed patients
- PMID: 38806543
- PMCID: PMC11133365
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62044-9
PMMA dialyzers modulate both humoral and cell-mediate immune response to anti-COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) in a cohort of chronic hemodialyzed patients
Abstract
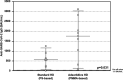
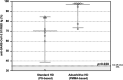
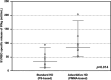
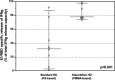
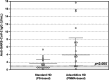
Patients on hemodialysis (HD) have a high risk of death from COVID-19. We evaluated the humoral and cell-mediated immune response to BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccine in HD patients, comparing HD with Poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) and HD with Polysulphone (PS). Samples were collected before vaccination (T0) and 14-days after the 2ndvaccine (T2) in a TG (TG, n = 16-Foggia) and in a VG (CG, n = 36-Novara). Anti-SARS-CoV-2-Ig were titrated in the cohort 2-weeks after the 2nddose of vaccine. In the Testing-Group, serum neutralizing antibodies (NAb) were assayed and PBMCs isolated from patients were thawed, counted and stimulated with SARS-CoV-2 IGRA stimulation tube set. All patients had a positive ab-response, except in a case. PMMA-patients had higher levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG (p = 0.031); VG data confirmed these findings (p < 0.05). NAb evaluation: PMMA patients passed the positive cut-off value, while in PS group only only 1/8 patient did not respond. PMMA patients showed higher percentages of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1/RBD-Ig after a complete vaccine schedule (p = 0.028). Interferon-gamma release: PMMA patients showed significantly higher release of IFNγ (p = 0.014). The full vaccination course provided sufficient protection against SARS-CoV-2 across the entire cohort, regardless of dialyzer type. After vaccination, PMMA patients show a better immune response, both humoral and cellular, at the end of the vaccination course than PS patients.
Keywords: Cellular immunity; Hemodialysis patients; Humoral immunity; Poly-methyl-methacrylate; SARS-CoV-2 vaccination; Vaccine antibody response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular and humoral immunogenicity of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in patients on haemodialysis.EBioMedicine. 2021 Aug;70:103524. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103524. Epub 2021 Aug 12. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34391096 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced T-cell immunity and lower humoral responses following 5-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with inborn errors of immunity compared with healthy controls.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 6;16:1538453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1538453. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40114918 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Infection on Humoral and Cellular Immunity in a Cohort of Patients with Immune-Mediated Diseases: A Pilot Study.Pathogens. 2024 Jun 14;13(6):506. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13060506. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38921803 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and risk factors for poor humoral immune response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with autoimmune hepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2024 Dec;116(12):671-679. doi: 10.17235/reed.2024.10053/2023. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2024. PMID: 38235657
-
Antibody response following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022 Feb;16(2):102406. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102406. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35104750 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chronic heart failure and hypoalbuminemia are risk factors of poorer mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine response in maintenance Hemodialysis patients (the COVaccinDia study).BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jun 23;26(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04264-3. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40551111 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

