Resistance to pyrethroids and the relationship between adult resistance and knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Aedes albopictus in dengue surveillance areas of Guizhou Province, China
- PMID: 38806622
- PMCID: PMC11133427
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63138-0
Resistance to pyrethroids and the relationship between adult resistance and knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Aedes albopictus in dengue surveillance areas of Guizhou Province, China
Abstract
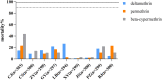
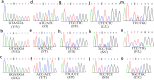
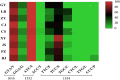
The Ae. albopictus mosquito has gained global attention due to its ability to transmit viruses, including the dengue and zika. Mosquito control is the only effective way to manage dengue fever, as no effective treatments or vaccines are available. Insecticides are highly effective in controlling mosquito densities, which reduces the chances of virus transmission. However, Ae. albopictus has developed resistance to pyrethroids in several provinces in China. Pyrethroids target the voltage-gated sodium channel gene (VGSC), and mutations in this gene may result in knockdown resistance (kdr). Correlation studies between resistance and mutations can assist viruses in managing Ae. albopictus, which has not been studied in Guizhou province. Nine field populations of Ae. albopictus at the larval stage were collected from Guizhou Province in 2022 and reared to F1 to F2 generations. Resistance bioassays were conducted against permethrin, beta-cypermethrin, and deltamethrin for both larvae and adults of Ae. albopictus. Kdr mutations were characterized by PCR and sequencing. Additionally, the correlation between the kdr allele and pyrethroid resistance was analyzed. All nine populations of Ae. albopictus larvae and adults were found to be resistant to three pyrethroid insecticides. One kdr mutant allele at codon 1016, one at 1532 and three at 1534 were identified with frequencies of 13.86% (V1016G), 0.53% (I1532T), 58.02% (F1534S), 11.69% (F1534C), 0.06% (F1534L) and 0.99% (F1534P), respectively. Both V1016G and F1534S mutation mosquitoes were found in all populations. The kdr mutation F1534S was positively correlated with three pyrethroid resistance phenotypes (OR > 1, P < 0.05), V1016G with deltamethrin and beta-cypermethrin resistance (OR > 1, P < 0.05) and F1534C only with beta-cypermethrin resistance (OR > 1, P < 0.05). Current susceptibility status of wild populations of Ae. albopictus to insecticides and a higher frequency of kdr mutations from dengue-monitored areas in Guizhou Province are reported in this paper. Outcomes of this study can serve as data support for further research and development of effective insecticidal interventions against Ae. albopictus populations in Guizhou Province.
Keywords: Ae. Albopictus; Kdr mutation; Dengue; Insecticide resistance; Pyrethroid.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
First identification of kdr allele F1534S in VGSC gene and its association with resistance to pyrethroid insecticides in Aedes albopictus populations from Haikou City, Hainan Island, China.Infect Dis Poverty. 2016 May 2;5:31. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0125-x. Infect Dis Poverty. 2016. PMID: 27133234 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrethroid resistance status and co-occurrence of V1016G, F1534C and S989P mutations in the Aedes aegypti population from two dengue outbreak counties along the China-Myanmar border.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Feb 27;17(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06124-9. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38414050 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae and adults to insecticides based on bioassays and knockdown resistance (kdr) mutations in Zhejiang Province, China.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Oct 1;284:117007. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117007. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39260213
-
Presence of the point mutations Val1016Gly in the voltage-gated sodium channel detected in a single mosquito from Panama.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jan 28;12(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3309-y. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30691518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrethroid resistance in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus: Important mosquito vectors of human diseases.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2016 Oct;133:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27742355 Review.
Cited by
-
[Effects of larval feeding amount on development and deltamethrin resistance in Aedes albopictus].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Mar 20;45(3):488-493. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.06. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40159963 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Zhang Y, et al. Resistance to three pyrethroid insecticides and knockdown resistance gene mutations in Aedes albopictus in Guiyang, Guizhou Province, China. Chin. J. Vect. Biol. Control. 2023;34:218–221.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

