Glucose and HODEs regulate Aspergillus ochraceus quorum sensing through the GprC-AcyA pathway
- PMID: 38806811
- PMCID: PMC11133280
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05160-z
Glucose and HODEs regulate Aspergillus ochraceus quorum sensing through the GprC-AcyA pathway
Abstract
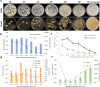
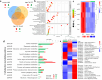
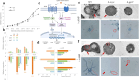
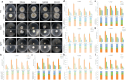
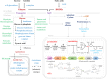
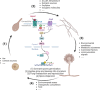
Aspergillus ochraceus is the traditional ochratoxin A (OTA)-producing fungus with density-dependent behaviors, which is known as quorum sensing (QS) that is mediated by signaling molecules. Individual cells trend to adapt environmental changes in a "whole" flora through communications, allowing fungus to occupy an important ecological niche. Signals perception, transmission, and feedback are all rely on a signal network that constituted by membrane receptors and intracellular effectors. However, the interference of density information in signal transduction, which regulates most life activities of Aspergillus, have yet to be elucidated. Here we show that the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) to cAMP pathway is responsible for transmitting density information, and regulates the key point in life cycle of A. ochraceus. Firstly, the quorum sensing phenomenon of A. ochraceus is confirmed, and identified the density threshold is 103 spores/mL, which represents the low density that produces the most OTA in a series quorum density. Moreover, the GprC that classified as sugar sensor, and intracellular adenylate cyclase (AcyA)-cAMP-PKA pathway that in response to ligands glucose and HODEs are verified. Furthermore, GprC and AcyA regulate the primary metabolism as well as secondary metabolism, and further affects the growth of A. ochraceus during the entire life cycle. These studies highlight a crucial G protein signaling pathway for cell communication that is mediated by carbohydrate and oxylipins, and clarified a comprehensive effect of fungal development, which include the direct gene regulation and indirect substrate or energy supply. Our work revealed more signal molecules that mediated density information and connected effects on important adaptive behaviors of Aspergillus ochraceus, hoping to achieve comprehensive prevention and control of mycotoxin pollution from interrupting cell communication.
Keywords: Cell communication; G protein–coupled receptor; Mycotoxin; Oxylipin; Second messenger.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no competing and conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aspergillus oxylipin signaling and quorum sensing pathways depend on g protein-coupled receptors.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Sep;4(9):695-717. doi: 10.3390/toxins4090695. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23105976 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Spore Density Has an Influence on Ochratoxin A Content in Aspergillus ochraceus CGMCC 3.4412 in PDB and Its Interaction with Seeds.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Apr 21;9(4):146. doi: 10.3390/toxins9040146. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28430142 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Catabolite Repression Gene AoCreA Regulates Morphological Development and Ochratoxin A Biosynthesis Responding to Carbon Sources in Aspergillus ochraceus.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 3;12(11):697. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110697. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33152993 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sensing mechanisms and targets for the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Sep;33(5):904-18. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01538.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10476026 Review.
-
Fungal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Promising Mediator of the Impact of Extracellular Signals on Biosynthesis of Ochratoxin A.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 12;12:631392. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.631392. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The rise of fungal G-protein coupled receptors in pathogenesis and symbiosis.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 12;21(6):e1013212. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013212. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40504784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 1993. (IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, No. 56.)
-
- Yang Q, Dhanasekaran S, Ngea GLN, Tian S, Li B, Zhang H. Unveiling ochratoxin a controlling and biodetoxification molecular mechanisms: Opportunities to secure foodstuffs from OTA contamination. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Nov;169:113437. 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113437. Epub 2022 Sep 20. PMID: 36165818. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

