A Systematic Review of Research Gaps in the Built Environment of Inpatient Healthcare Settings
- PMID: 38807411
- PMCID: PMC11491052
- DOI: 10.1177/19375867241251830
A Systematic Review of Research Gaps in the Built Environment of Inpatient Healthcare Settings
Abstract
Objective: This study utilized the evidence-gap map method and critically examined the scope, methodologies, and focus of the studies that investigated the influence of the built environment on inpatient healthcare settings over a decade (2010-2021).
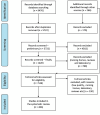
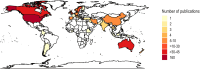
Methods: We conducted a systematic review per the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses guidelines and surveyed 406 articles, primarily from North America and Europe.
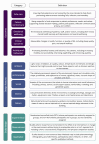
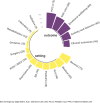
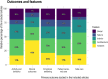
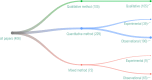
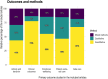
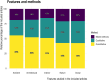
Results: Our findings revealed a dominant focus on architectural features (73%), such as room design and ward layout. Comparatively, there was less emphasis on interior-, ambient-, social-, and nature-related features. Most previous studies explored multiple environmental features, which indicated the intricacy of this field. Research outcomes were diverse, with person-centered care (PCC) being the most frequently investigated, followed by safe care, emotional well-being, activity, and behavior. Furthermore, research methods varied considerably based on the study's outcomes and features. Clinical outcomes and safe care favored quantitative methods, activity and behavior favored mixed methods, and PCC favored qualitative research.
Conclusion: This review provides an in-depth overview of the existing studies on healthcare design research and sheds light on the current trends and methodological choices. The insights garnered can guide future research, policy-making, and the development of healthcare facilities.
Keywords: built environment; evidence-based design; evidence-gap map; healthcare architecture; healthcare settings; hospital; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Brambilla A., Rebecchi A., Capolongo S. (2019). Evidence based hospital design. A literature review of the recent publications about the EBD impact of built environment on hospital occupants’ and organizational outcomes. Annali Di Igiene, 31(2), 165–180. https://doi:10.7416/ai.2019.2269 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

