miR‑576‑3p/M‑phase phosphoprotein 8 axis regulates the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 38807669
- PMCID: PMC11130756
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14460
miR‑576‑3p/M‑phase phosphoprotein 8 axis regulates the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
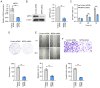
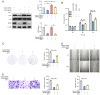
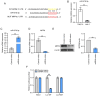
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a fatal digestive system cancer with unclear pathogenesis. M-phase phosphoprotein 8 (MPP8) has been shown to play a vital role in several cancer types, such as non-small cell lung cancer, gastric cancer and melanoma; however, there have been no studies into its role in HCC. The present study aimed to evaluate the role of MPP8 in regulating malignant phenotypes of liver cancer cells, and to further investigate the underlying mechanism. Bioinformatics analysis was performed to analyze related data from a public database, and to predict the potential microRNAs (miRNAs) that might target MPP8 mRNA; reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was used to measure the levels of mRNA and miRNA; western blotting was employed to detect protein levels; Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and plate colony formation assays, wound healing assay and Transwell invasion assay were performed to evaluate the ability of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, respectively; dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was performed to identify the target association. The results showed that MPP8 was a risk factor for the survival of patients with HCC, and was up-regulated in HCC tissue samples and cell lines; MPP8 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of liver cancer cells; MPP8 knockdown suppressed the PI3K/Akt pathway, and activation of this pathway reversed the inhibited liver cancer cell phenotypes by down-regulating MPP8; miR-576-3p, which was low in liver cancer cells, negatively regulated MPP8 expression by directly targeting its mRNA; up-regulating MPP8 expression reversed the inhibited signaling pathway and malignant phenotypes of liver cancer cells by miR-576-3p overexpression. In conclusion, the miR-576-3p/MPP8 axis regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of liver cancer cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. These findings lead novel insights into HCC progression, and propose MPP8 as a potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: M-phase phosphoprotein 8; PI3K/Akt pathway; hepatocellular carcinoma; malignant phenotype; miR-576-3p.
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SPRR3, a novel miR-338-3p target, regulates the malignant progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in vitro via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):317. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11246. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35350667 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA RHPN1-AS1 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion Through Targeting miR-7-5p and Activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820957023. doi: 10.1177/1533033820957023. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. Retraction in: Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231178771. doi: 10.1177/15330338231178771. PMID: 32910747 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Downregulation of N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase GCNT3 by miR-302b-3p Decreases Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):987-1004. doi: 10.1159/000494482. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355927
-
CircCCNB1 silencing acting as a miR-106b-5p sponge inhibited GPM6A expression to promote HCC progression by enhancing DYNC1I1 expression and activating the AKT/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):637-651. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66915. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002514 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-depleted MiR-148a-3p derived from Hepatic Stellate Cells Promotes Tumor Progression via ITGA5/PI3K/Akt Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 6;18(6):2249-2260. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66184. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35414782 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic reader chromodomain as a potential therapeutic target.RSC Chem Biol. 2025 Apr 11;6(6):833-844. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00324a. eCollection 2025 Jun 4. RSC Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40302984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chapiro J, Duran R, Lin MD, Schernthaner RE, Wang Z, Gorodetski B, Geschwind JF. Identifying staging markers for hepatocellular carcinoma before transarterial chemoembolization: Comparison of three-dimensional quantitative versus non-three-dimensional imaging markers. Radiology. 2015;275:438–447. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14141180. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
