Value of exhaled hydrogen sulfide in early diagnosis of esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38807679
- PMCID: PMC11130606
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14454
Value of exhaled hydrogen sulfide in early diagnosis of esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma
Abstract
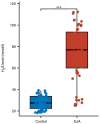
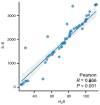
Esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma (EJA) has increased in recent years, and it exhibits a poor prognosis and a short survival period for patients. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cancer and has been studied as a diagnostic factor in some tumor diseases. However, few studies have explored the diagnostic value of H2S for EJA. In the present study, a total of 56 patients with early-stage EJA were enrolled while 57 healthy individuals were selected as the healthy control group. Clinical features were recorded, and exhaled H2S and blood samples were collected from both groups. Exhaled H2S and serum interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression levels were detected in both groups. The correlation between exhaled H2S and serum IL-8 levels was analyzed using Pearson's correlation method. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of exhaled H2S combined with IL-8 detection in EJA. The results showed that patients with EJA exhaled more H2S than healthy individuals. In addition, exhaled H2S was positively correlated with increased IL-8 expression. The ROC curve revealed that the exhaled H2S test had an acceptable diagnostic effect and could be used to diagnose EJA. The increase in H2S exhaled by patients with EJA indicated that H2S may be related to the occurrence and development of EJA; however, the in vivo mechanism needs to be further explored. Collectively, it was determined in the present study that exhaled H2S was significantly higher in patients with early-stage EJA than in healthy controls and combined diagnosis with patient serum IL-8 could improve diagnostic accuracy, which has potential diagnostic value for early diagnosis and screening of EJA.
Keywords: cancer; diagnosis; esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma; exhaled hydrogen sulfide; interleukin-8.
Copyright: © 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zhao JJ, Liu FL. Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy and lymph node resection in adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;25:114–119. (In Chinese) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
