Efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with desmoid fibromatosis: a retrospective analysis
- PMID: 38807768
- PMCID: PMC11130419
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1399574
Efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with desmoid fibromatosis: a retrospective analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Desmoid fibromatosis is an aggressive fibroblastic neoplasm with a high propensity for local recurrence. Targeted therapy for Desmoid fibromatosis represents a novel avenue in systemic treatment. Anlotinib, a novel multitargeted angiogenesis inhibitor, represents a novel approach for targeted therapy. Therefore, this study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with Desmoid fibromatosis.
Methods: We retrospectively gathered the clinical medical records of Desmoid fibromatosis patients who underwent anlotinib treatment between June 2019 and November 2023 at our center. Anlotinib was initiated at a daily dose of 12 mg and adjusted based on drug-related toxicity. Tumor response was evaluated using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1 criteria. Progression-free survival served as the primary endpoint and was analyzed utilizing the Kaplan-Meier method.
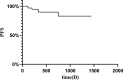
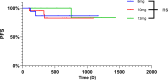
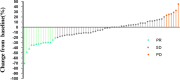
Results: In total, sixty-six consecutive patients were enrolled. No patients achieved a complete response; however, fourteen patients (21.21%) exhibited a partial response, while forty-six patients (70%) experienced disease stability. Progressive disease was observed in 6 patients (9.10%), and the progression-free survival rates at 12 and 36months were 89.71% and 82.81%, respectively. The disease control rate was 90.91%, while the objective response rate was 21.21%.
Conclusion: Anlotinib proves effective in managing recurrent and symptomatic patients with Desmoid fibromatosis. However, the toxicity profile of anlotinib presents a higher risk of Hand-Foot Skin Reaction and hypertension. Therefore, given that 41.67% of patients were subjected to dose adjustments associated with the initial dose of 12 mg, implementing dosage reductions may help balance efficacy with side effects.
Keywords: anlotinib; desmoid fibromatosis; dosage adjustments; targeted therapy; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024 Xie, Huang, Gong, Wang, Li, Lu, Luo, Min, Zhou and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Activity and Safety of Anlotinib for Patients with Extremity Desmoid Fibromatosis: A Retrospective Study in a Single Institution.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Sep 25;14:3941-3950. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S271008. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33061299 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery combined with anlotinib for local control of patients with resectable extremity desmoid fibromatosis: a retrospective study.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 7;15:1357071. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1357071. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38515843 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Anlotinib and Celecoxib for the Treatment of Abdominal Desmoid Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 13;11:830672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.830672. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35096630 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Sporadic Desmoid Tumours and Its Implications for Novel Therapies: A Systematised Narrative Review.Target Oncol. 2022 May;17(3):223-252. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00876-z. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Target Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35446005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of doxorubicin-based and liposomal doxorubicin chemotherapies for patients with extra-abdominal desmoid-type fibromatosis: a systematic review.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;50(11):1274-1281. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyaa125. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32700733
References
-
- Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F. editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press. (2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources