Quantification of the Anti-diabetic Effect of Allium cepa
- PMID: 38807798
- PMCID: PMC11130450
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59174
Quantification of the Anti-diabetic Effect of Allium cepa
Abstract
Background: Allium cepa, or onion, boosts numerous health benefits, including anti-diabetic effects. Its rich array of antioxidants and sulfur compounds not only aids heart health by lowering cholesterol and blood pressure but also exhibits anti-inflammatory properties. Onion's antibacterial and antiviral properties help combat infections, while its compounds like quercetin show promise in cancer prevention. Additionally, Allium cepa supports respiratory health by relieving coughs and colds and aids digestion with its prebiotic properties. Incorporating onions into a balanced diet can enhance overall well-being, including managing blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
Aim and objective: This study aims to determine if the ethanolic extract from the dried peel of Allium cepa holds potential as an anti-diabetic agent, with a focus on its ability to manage diabetes and reduce blood sugar levels.
Methodology: To prepare the ethanolic extract from dried onion peel, the peel was finely ground and soaked in ethanol. The mixture was then agitated and filtered to separate the liquid extract. Finally, the filtrate was concentrated using methods such as rotary evaporation or vacuum distillation to obtain a concentrated extract for further analysis like alpha-amylase inhibition assay and alpha-glucosidase inhibition assay.
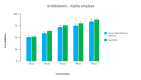
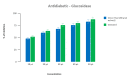
Results: The ethanolic extracts derived from dried onion peel demonstrate inhibition of alpha-glucosidase, leading to reduced blood glucose levels. Additionally, this inhibition prompts an increase in insulin production.
Conclusion: The study underscores that the efficacy of the ethanolic extract of dried onion peel increases with concentration. It highlights the presence of beneficial compounds like total phenolics, flavonoids, quercetin, and its derivatives in onion peel, known for their therapeutic roles in cardiovascular health, weight management, diabetes control, cancer prevention, and antimicrobial activity. These findings affirm the hypoglycemic and anti-diabetic properties of Allium cepa's ethanolic leaf extract.
Keywords: alpha-amylase inhibition; alpha-glucosidase inhibition; anti-diabetic effect; blood glucose level; ethanolic extract; onion peel.
Copyright © 2024, Esakki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Unveiling causal connections: Long-term particulate matter exposure and type 2 diabetes mellitus mortality in Southern China. Guo T, Cheng X, Wei J, et al. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;274:116212. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
