Development of White Cabbage, Coffee, and Red Onion Extracts as Natural Phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B) Inhibitors for Cognitive Dysfunction: In Vitro and In Silico Studies
- PMID: 38808119
- PMCID: PMC11132833
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/1230239
Development of White Cabbage, Coffee, and Red Onion Extracts as Natural Phosphodiesterase-4B (PDE4B) Inhibitors for Cognitive Dysfunction: In Vitro and In Silico Studies
Abstract
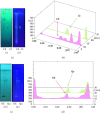
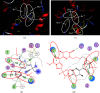
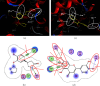
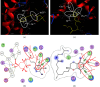
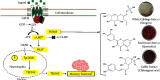
Human cognition fundamentally depends on memory. Alzheimer's disease exhibits a strong correlation with a decline in this factor. Phosphodiesterase-4 B (PDE4B) plays a crucial role in neurodegenerative disorders, and its inhibition is one of the promising approaches for memory enhancement. This study aimed to identify secondary metabolites in white cabbage, coffee, and red onion extracts and identify their molecular interaction with PDE4B by in silico and in vitro experiments. Crushed white cabbage and red onion were macerated separately with ethanol to yield respective extracts, and ground coffee was boiled with water to produce aqueous extract. Thin layer chromatography (TLC)-densitometry was used to examine the phytochemicals present in white cabbage, coffee, and red onion extracts. Molecular docking studies were performed to know the interaction of test compounds with PDE4B. TLC-densitometry analysis showed that chlorogenic acid and quercetin were detected as major compounds in coffee and red onion extracts, respectively. In silico studies revealed that alpha-tocopherol (binding free energy (∆Gbind) = -38.00 kcal/mol) has the strongest interaction with PDE4B whereas chlorogenic acid (∆Gbind = -21.50 kcal/mol) and quercetin (∆Gbind = -17.25 kcal/mol) exhibited moderate interaction. In vitro assay showed that the combination extracts (cabbage, coffee, and red onion) had a stronger activity (half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) = 0.12 ± 0.03 µM) than combination standards (sinigrin, chlorogenic acid, and quercetin) (IC50 = 0.17 ± 0.03 µM) and rolipram (IC50 = 0.15 ± 0.008 µM). Thus, the combination extracts are a promising cognitive enhancer by blocking PDE4B activity.
Copyright © 2024 Nazir Ahmad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Quercetin Rich Onion Extracts on Bacterial Quorum Sensing.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 24;10:867. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00867. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31105665 Free PMC article.
-
Insecticidal Activity of Organic Extracts of Solidago graminifolia and Its Main Metabolites (Quercetin and Chlorogenic Acid) against Spodoptera frugiperda: An In Vitro and In Silico Approach.Molecules. 2022 May 22;27(10):3325. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103325. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630802 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Water Molecules in the Ligand Binding Domain of PDE4B and PDE4D: Virtual Screening Based Molecular Docking of Some Active Scaffolds.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2019;15(4):334-366. doi: 10.2174/1573409914666181105153543. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2019. PMID: 30394213
-
Phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) inhibitors and their applications in recent years (2014 to early 2025).Mol Divers. 2025 Jun 14. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11242-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40515964 Review.
-
Recent advances of Phosphodiesterase 4B in cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023 Feb;27(2):121-132. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2023.2183496. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023. PMID: 36803246 Review.
References
-
- Fakhrudin N., Fakhrudin N., Nurrochmad A., Sudarmanto B. S. A., Ikawati Z. In vitro and in silico studies of secang wood (Caesalpinia sappan L.) extracts and Brazilin as natural phosphodiesterase-1 (PDE1) inhibitor for herbal cognitive enhancer development. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology . 2020;13(5):2269–2274. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00409.6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
