Superior Drug Delivery Performance of Multifunctional Bilosomes: Innovative Strategy to Kill Skin Cancer Cells for Nanomedicine Application
- PMID: 38808148
- PMCID: PMC11131132
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S450181
Superior Drug Delivery Performance of Multifunctional Bilosomes: Innovative Strategy to Kill Skin Cancer Cells for Nanomedicine Application
Abstract
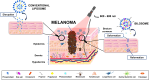
Purpose: Numerous failures in melanoma treatment as a highly aggressive form of skin cancer with an unfavorable prognosis and excessive resistance to conventional therapies are prompting an urgent search for more effective therapeutic tools. Consequently, to increase the treatment efficiency and to reduce the side effects of traditional administration ways, herein, it has become crucial to combine photodynamic therapy as a promising therapeutic approach with the selectivity and biocompatibility of a novel colloidal transdermal nanoplatform for effective delivery of hybrid cargo with synergistic effects on melanoma cells.
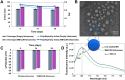
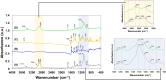
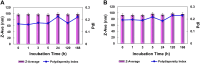
Methods: The self-assembled bilosomes, co-stabilized with L-α-phosphatidylcholine, sodium cholate, Pluronic® P123, and cholesterol, were designated, and the stability of colloidal vesicles was studied using dynamic and electrophoretic light scattering, also provided in cell culture medium (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium). The hybrid compounds - a classical photosensitizer (Methylene Blue) along with a complementary natural polyphenolic agent (curcumin), were successfully co-loaded, as confirmed by UV-Vis, ATR-FTIR, and fluorescent spectroscopies. The biocompatibility and usefulness of the polymer functionalized bilosome with loaded double cargo were demonstrated in vitro cyto- and phototoxicity experiments using normal keratinocytes and melanoma cancer cells.
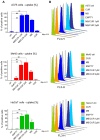
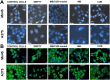
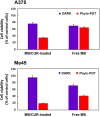
Results: The in vitro bioimaging and immunofluorescence study upon human skin epithelial (A375) and malignant (Me45) melanoma cell lines established the protective effect of the PEGylated bilosome surface. This effect was confirmed in cytotoxicity experiments, also determined on human cutaneous (HaCaT) keratinocytes. The flow cytometry experiments indicated the enhanced uptake of the encapsulated hybrid cargo compared to the non-loaded MB and CUR molecules, as well as a selectivity of the obtained nanocarriers upon tumor cell lines. The phyto-photodynamic action provided 24h-post irradiation revealed a more significant influence of the nanoplatform on Me45 cells in contrast to the A375 cell line, causing the cell viability rate below 20% of the control.
Conclusion: As a result, we established an innovative and effective strategy for potential metastatic melanoma treatment through the synergism of phyto-photodynamic therapy and novel bilosomal-origin nanophotosensitizers.
Keywords: A375 cells; Me45 cells; antitumor activity; human melanoma; nanovesicular carriers; phyto-photodynamic therapy.
© 2024 Waglewska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper declare no competing financial or other interests that could affect the work they describe here.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial phyto-photodynamic activity inducing by polyphenol-supported Methylene Blue co-loaded into multifunctional bilosomes: Advanced hybrid nanoplatform in the skin infections treatment?J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023 Mar;240:112650. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2023.112650. Epub 2023 Jan 14. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2023. PMID: 36701884
-
Selective Photodynamic Effects on Breast Cancer Cells Provided by p123 Pluronic®- Based Nanoparticles Modulating Hypericin Delivery.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(11):1352-1367. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666181102091010. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30387402
-
Effects of curcumin based PDT on the viability and the organization of actin in melanotic (A375) and amelanotic melanoma (C32) - in vitro studies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Dec;132:110883. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110883. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33113417
-
Photodynamic Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma Treatment: A Review.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan 1;17:1533033818791795. doi: 10.1177/1533033818791795. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 30099929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanophotosensitizers toward advanced photodynamic therapy of Cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jul 1;334(2):176-87. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.09.012. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23017942 Review.
Cited by
-
In-vivo and in-vitro assessment of curcumin loaded bile salt stabilized nanovesicles for oral delivery.Daru. 2024 Dec 23;33(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s40199-024-00544-9. Daru. 2024. PMID: 39714544
-
Bilosomal Encapsulation of Binuclear Phosphino Ru(II)-Cu(II) Compounds Enhances Their Selectivity and Activity toward Lung and Prostate Cancers.J Med Chem. 2025 Jul 24;68(14):14442-14464. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5c00486. Epub 2025 Jul 9. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40631712 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular Carriers for Phytochemical Delivery: A Comprehensive Review of Techniques and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 2;17(4):464. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040464. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fan L, Wang Z, Shi D. Targeted nanoscale drug delivery systems for melanoma therapy. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023;86:104724. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104724 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

