Predictors of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome and the optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy
- PMID: 38808215
- PMCID: PMC11132419
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_452_22
Predictors of gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome and the optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy
Abstract
Background: This study aims to estimate the risk factors of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and to evaluate the optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT).
Materials and methods: We enrolled 1266 patients with ACS in a telephone follow-up program to determine whether any of the patients were hospitalized for GI bleeding. We collected baseline data, laboratory tests, electrocardiograms, and echocardiography covering all ACS patients. Multivariable regression was performed to adjust for confounders and predictors of GI bleeding. At the same time, the optimal duration of DAPT for ACS patients was evaluated.
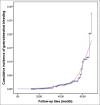
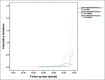
Results: A total of 1061 ACS patients were included in the study. After 13-68 months, 48 patients (4.5%) were hospitalized for GI bleeding. The risk of GI bleeding was significantly increased in patients treated with DAPT for more than 18 months (hazard ratio 12.792, 5.607-29.185, P < 0.01). Receiver Operating Characteristic curve showed that the duration of DAPT using a cutoff of 14.5 months resulted in a sensitivity of 66.7% and a specificity of 77%.
Conclusion: In patients with ACS, DAPT time are the main risk factors of GI bleeding. The optimal duration of DAPT is 14.5 months.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; dual antiplatelet therapy; gastrointestinal bleeding.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of one-month versus twelve-month dual antiplatelet therapy after implantation of drug-eluting stents guided by either intravascular ultrasound or angiography in patients with acute coronary syndrome: rationale and design of prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled IVUS-ACS and ULTIMATE-DAPT trial.Am Heart J. 2021 Jun;236:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2021.02.014. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Am Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33621541
-
Impact of age on the comparison between short-term vs 12-month dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with the COMBO dual therapy stent: 2-Year follow-up results of the REDUCE trial.Atherosclerosis. 2021 Mar;321:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Atherosclerosis. 2021. PMID: 33639478 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dual antiplatelet therapy prolongation in acute coronary syndrome patients with both high ischemic and bleeding risk: insight from the OPT-CAD study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 8;10:1201091. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1201091. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37745130 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of short-term or prolonged as compared to standard 1 year DAPT in patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with drug-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of 9 randomized trials.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Aug;50(2):337-354. doi: 10.1007/s11239-019-02033-2. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 31919736
-
Strategies to Optimize Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Coronary Artery Stenting in Acute Coronary Syndrome.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jul;22(4):347-355. doi: 10.1177/1074248416683048. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28587584 Review.
References
-
- Lau LH, Sung JJ. Treatment of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in 2020: New techniques and outcomes. Dig Endosc. 2021;33:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Pioppo L, Bhurwal A, Reja D, Tawadros A, Mutneja H, Goel A, et al. Incidence of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding worsens outcomes with acute coronary syndrome: Result of a national cohort. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:999–1008. - PubMed
-
- Pemmasani G, Elgendy I, Mamas MA, Leighton JA, Aronow WS, Tremaine WJ. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease presenting with acute coronary syndrome. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021;27:1017–25. - PubMed
-
- Hao Y, Liu J, Liu J, Smith SC, Jr., Huo Y, Fonarow GC, et al. Rationale and design of the improving care for cardiovascular disease in China (CCC) project: A national effort to prompt quality enhancement for acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. 2016;179:107–15. - PubMed
-
- Khan MY, Siddiqui WJ, Alvarez C, Aggarwal S, Hasni SF, Ahmad A, et al. Reduction in postpercutaneous coronary intervention angina in addition to gastrointestinal events in patients on combined proton pump inhibitors and dual antiplatelet therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30:847–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
