Structural and Biochemical Requirements for Secretory Component Interactions with Dimeric IgA
- PMID: 38809110
- PMCID: PMC11233122
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300717
Structural and Biochemical Requirements for Secretory Component Interactions with Dimeric IgA
Abstract
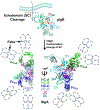
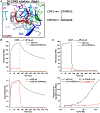
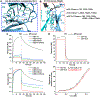
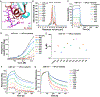
Secretory (S) IgA is the predominant mucosal Ab that protects host epithelial barriers and promotes microbial homeostasis. SIgA production occurs when plasma cells assemble two copies of monomeric IgA and one joining chain (JC) to form dimeric (d) IgA, which is bound by the polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR) on the basolateral surface of epithelial cells and transcytosed to the apical surface. There, pIgR is proteolytically cleaved, releasing SIgA, a complex of the dIgA and the pIgR ectodomain, called the secretory component (SC). The pIgR's five Ig-like domains (D1-D5) undergo a conformational change upon binding dIgA, ultimately contacting four IgA H chains and the JC in SIgA. In this study, we report structure-based mutational analysis combined with surface plasmon resonance binding assays that identify key residues in mouse SC D1 and D3 that mediate SC binding to dIgA. Residues in D1 CDR3 are likely to initiate binding, whereas residues that stabilize the D1-D3 interface are likely to promote the conformational change and stabilize the final SIgA structure. Additionally, we find that the JC's three C-terminal residues play a limited role in dIgA assembly but a significant role in pIgR/SC binding to dIgA. Together, these results inform models for the intricate mechanisms underlying IgA transport across epithelia and functions in the mucosa.
Copyright © 2024 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
Update of
-
Structural and biochemical requirements for secretory component interactions with dimeric Immunoglobulin A.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 17:2023.11.09.566401. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566401. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Immunol. 2024 Jul 15;213(2):226-234. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300717. PMID: 38014291 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Structural and biochemical requirements for secretory component interactions with dimeric Immunoglobulin A.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 17:2023.11.09.566401. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566401. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Immunol. 2024 Jul 15;213(2):226-234. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300717. PMID: 38014291 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Increased immunoglobulin A levels in milk by over-expressing the murine polymeric immunoglobulin receptor gene in the mammary gland epithelial cells of transgenic mice.Immunology. 2000 Oct;101(2):218-24. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00094.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 11012775 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor.J Oral Sci. 2011 Jun;53(2):147-56. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.53.147. J Oral Sci. 2011. PMID: 21712618 Review.
-
Immunoglobulin A/PIGR axis as potential mediators of human abdominal aortic aneurysms revealed by topologically resolved proteomics.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 7;23(1):747. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06758-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40624587 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) in cancer progression: a critical role and potential therapeutic target.Apoptosis. 2025 Aug;30(7-8):1751-1775. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02116-x. Epub 2025 May 26. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40415061 Review.
References
-
- Zikan J, Mestecky J, Kulhavy R, and Bennett JC. 1986. The stoichiometry of J chain in human secretory dimeric IgA. Molecular Immunology 23: 541–544. - PubMed
-
- Lombana TN, Rajan S, Zorn JA, Mandikian D, Chen EC, Estevez A, Yip V, Bravo DD, Phung W, Farahi F, Viajar S, Lee S, Gill A, Sandoval W, Wang J, Ciferri C, Boswell CA, Matsumoto ML, and Spiess C. 2019. Production, characterization, and in vivo half-life extension of polymeric IgA molecules in mice. mAbs 11: 1122–1138. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

