Sialic Acid-Siglec-E Interactions Regulate the Response of Neonatal Macrophages to Group B Streptococcus
- PMID: 38809232
- PMCID: PMC11150127
- DOI: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2300076
Sialic Acid-Siglec-E Interactions Regulate the Response of Neonatal Macrophages to Group B Streptococcus
Abstract
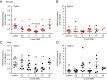
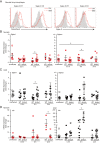
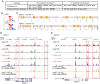
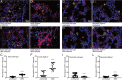
The mammalian Siglec receptor sialoadhesin (Siglec1, CD169) confers innate immunity against the encapsulated pathogen group B Streptococcus (GBS). Newborn lung macrophages have lower expression levels of sialoadhesin at birth compared with the postnatal period, increasing their susceptibility to GBS infection. In this study, we investigate the mechanisms regulating sialoadhesin expression in the newborn mouse lung. In both neonatal and adult mice, GBS lung infection reduced Siglec1 expression, potentially delaying acquisition of immunity in neonates. Suppression of Siglec1 expression required interactions between sialic acid on the GBS capsule and the inhibitory host receptor Siglec-E. The Siglec1 gene contains multiple STAT binding motifs, which could regulate expression of sialoadhesin downstream of innate immune signals. Although GBS infection reduced STAT1 expression in the lungs of wild-type newborn mice, we observed increased numbers of STAT1+ cells in Siglece-/- lungs. To test if innate immune activation could increase sialoadhesin at birth, we first demonstrated that treatment of neonatal lung macrophages ex vivo with inflammatory activators increased sialoadhesin expression. However, overcoming the low sialoadhesin expression at birth using in vivo prenatal exposures or treatments with inflammatory stimuli were not successful. The suppression of sialoadhesin expression by GBS-Siglec-E engagement may therefore contribute to disease pathogenesis in newborns and represent a challenging but potentially appealing therapeutic opportunity to augment immunity at birth.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nanduri, S. A., Petit S., Smelser C., Apostol M., Alden N. B., Harrison L. H., Lynfield R., Vagnone P. S., Burzlaff K., Spina N. L., et al. 2019. Epidemiology of invasive early-onset and late-onset group B streptococcal disease in the United States, 2006 to 2015: multistate laboratory and population-based surveillance. JAMA Pediatr. 173: 224–233. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Francois Watkins, L. K., McGee L., Schrag S. J., Beall B., Jain J. H., Pondo T., Farley M. M., Harrison L. H., Zansky S. M., Baumbach J., et al. 2019. Epidemiology of invasive group B streptococcal infections among nonpregnant adults in the United States, 2008-2016. JAMA Intern. Med. 179: 479–488. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Joshi, N., Walter J. M., Misharin A. V.. 2018. Alveolar macrophages. Cell. Immunol. 330: 86–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

