Efficacy and safety of Zhishixiaopi decoction in functional dyspepsia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38809916
- PMCID: PMC11135732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301686
Efficacy and safety of Zhishixiaopi decoction in functional dyspepsia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Functional dyspepsia (FD) refers to a group of clinical symptoms caused by gastric and duodenal dysfunction. Which is a chronic functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract with no cure. Zhishixiaopi decoction (ZSXP) is a type of Chinese herbal prescription that for treating FD. Although some randomized controlled trials (RCTs) report that ZSXP can significantly improve FD clinical symptoms and/or laboratory results, the trial design varies greatly among studies, making it challenging to draw a conclusion of the efficacy of ZSXP in treating FD.
Design: A systematic review and a meta-analysis.
Setting: Mianyang Central Hospital.
Objective: We conducted a systematic review and a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ZSXP for treating FD.
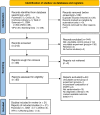
Methods: We developed inclusion and exclusion criteria based on FD diagnosed criteria, interventions to treat FD, and outcomes of these interventions. Search strategies combined disease terms, symptom terms, anatomy terms and intervention terms. Literature search was conducted on eight online databases in English or Chinese, including Medline (via PubMed), Embase (via Ovid), The Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China Biology Medicine (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Scientific Journals Database (VIP), and Wanfang Database.
Intervention: The experimental group received oral administration of ZSXP and had a complete treatment process. ZSXP needs to fully contain the key herbal ingredients, regardless of whether the dosage of each herb is consistent with the original prescription. The Control group received monotherapy or combination therapy of other Western medicine and had a complete treatment process.
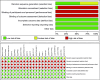
Outcomes: The primary outcomes appraised were Total effective rate (TER), serum levels of Motilin(MOT), Gastrin(GAS) and Somatostatin (SS), Gastric emptying rate (GER) using a Barium meal method (GER(B)) and Gastric half emptying time using an Ultrasonic method (GHET(T1/2)). The Cochrane Bias Risk Tool was used for quality critical appraisal, Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.3 was used for statistical analysis.
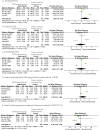
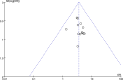
Results: A total of 21 medium-quality RCTs were included in the meta-analysis. All 21 included studies were conducted and completed in Mainland China from 1998 to 2020. The treatment duration was between two weeks to two months. The meta-analysis suggests that, compared with the Western medicine treatment group, ZSXP treatment was more effective to improving the TER in FD [Odds ratio, OR = 3.54, 95%CI:(2.49, 5.05), Z = 6.99, P<0.00001] without significant increase in adverse events. However, no statistical significance was found between the groups in serum MOT levels [Standard mean difference, SMD = 1.05, 95%CI:(-0.42, 2.53), Z = 1.04, P = 0.16], serum GAS levels [SMD = -0.16, 95%CI:(-1.20, 0.88), Z = 0.31, P = 0.76], serum SS levels [SMD = -0.04, 95%CI:(-1.97, 1.89), Z = 0.04, P = 0.97], GER(B) [SMD = 1.09, 95%CI:(-0.81, 3.00), Z = 1.12, P = 0.26]or GHET(T1/2) [Mean difference, MD = -2.18, 95%CI:(-5.55, 1.19), Z = 1.27, P = 0.20].
Conclusions: The meta-analysis suggests that Zhishixiaopi treatment is a relatively effective and safe traditional Chinese medicine prescription and could be used for functional dyspepsia treatment. Considering the limitations of this study, the conclusion needs to be further confirmed by high-quality, multi-center, and large-sample randomized controlled trials.
Copyright: © 2024 Zhao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Functional Dyspepsia With Psychological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 14;16:933290. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.933290. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35911981 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of Xin kai bitter method in the treatment of functional dyspepsia.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 May;9(3):993-1003. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-860. Epub 2020 May 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32434358
-
Herbal medicine Banha-sasim-tang for the treatment of functional dyspepsia protocol for a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(22):e15760. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015760. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31145294 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the herbal medicine Rikkunshito, for functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jan;36(1):64-74. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15208. Epub 2020 Aug 17. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 32767596 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine Siho-sogan-san for functional dyspepsia: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 25;99(39):e22358. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022358. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32991452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aziz I, Palsson OS, Törnblom H, Sperber AD, Whitehead WE, Simrén M. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and associations for symptom-based Rome IV functional dyspepsia in adults in the USA, Canada, and the UK: a cross-sectional population-based study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(4):252–62. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30003-7 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

