Post-GWAS multiomic functional investigation of the TNIP1 locus in Alzheimer's disease highlights a potential role for GPX3
- PMID: 38809917
- PMCID: PMC11247664
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13848
Post-GWAS multiomic functional investigation of the TNIP1 locus in Alzheimer's disease highlights a potential role for GPX3
Abstract
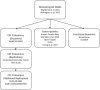
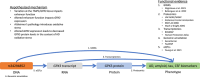
Introduction: Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have reported a genetic association with Alzheimer's disease (AD) at the TNIP1/GPX3 locus, but the mechanism is unclear.
Methods: We used cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteomics data to test (n = 137) and replicate (n = 446) the association of glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) with CSF biomarkers (including amyloid and tau) and the GWAS-implicated variants (rs34294852 and rs871269).
Results: CSF GPX3 levels decreased with amyloid and tau positivity (analysis of variance P = 1.5 × 10-5) and higher CSF phosphorylated tau (p-tau) levels (P = 9.28 × 10-7). The rs34294852 minor allele was associated with decreased GPX3 (P = 0.041). The replication cohort found associations of GPX3 with amyloid and tau positivity (P = 2.56 × 10-6) and CSF p-tau levels (P = 4.38 × 10-9).
Discussion: These results suggest variants in the TNIP1 locus may affect the oxidative stress response in AD via altered GPX3 levels.
Highlights: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) levels decreased with amyloid and tau positivity and higher CSF phosphorylated tau. The minor allele of rs34294852 was associated with lower CSF GPX3. levels when also controlling for amyloid and tau category. GPX3 transcript levels in the prefrontal cortex were lower in Alzheimer's disease than controls. rs34294852 is an expression quantitative trait locus for GPX3 in blood, neutrophils, and microglia.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; genome‐wide association studies; genomics; glutathione peroxidase 3; proteomics.
© 2024 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
C.C. receives research support from Biogen, EISAI, Alector, GSK and Parabon; these funders of the study had no role in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the paper for publication. C.C. is a member of the advisory board of Vivid Genomics, Halia Therapeutics, and ADx Healthcare. H.Z. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Alector, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Pinteon Therapeutics, Red Abbey Labs, Passage Bio, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. K.B. has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, BioArctic, Biogen, Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. G.K. is a full‐time employee of Roche Diagnostics GmbH. M.C. is a full‐time employee and shareholder of Roche Diagnostics International Ltd. N.W. is a full‐time employee of Roche Diagnostics GmbH. S.C.J. serves as a consultant to Roche Diagnostics and receives research funding from Cerveau Technologies. M.P.S. is a cofounder and scientific advisor of Personalis, SensOmics, Qbio, January AI, Fodsel, Filtricine, Protos, RTHM, Iollo, Marble Therapeutics, Crosshair Therapeutics, NextThought, and Mirvie. He is a scientific advisor of Jupiter, Neuvivo, Swaza, Mitrix, Yuvan, TranscribeGlass, and Applied Cognition. Other authors have no competing interests to declare. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Risk as a Marker of Amyloid-β and Tau Burden in Cerebrospinal Fluid.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(4):1417-1427. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160707. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27834776 Free PMC article.
-
Chitinase-3-like 1 protein (CHI3L1) locus influences cerebrospinal fluid levels of YKL-40.BMC Neurol. 2016 Nov 10;16(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0742-9. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27832767 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct CSF α-synuclein aggregation profiles associated with Alzheimer's disease phenotypes and MCI-to-AD conversion.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Feb;12(2):100040. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2024.100040. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39863324 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42, t-tau, and p-tau levels in the differential diagnosis of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2017 May 10;14(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12987-017-0062-5. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2017. PMID: 28486988 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Profiling and Therapeutic Targeting of Oxidative Stress in Autoimmune Encephalitis.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;75(2):38. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02332-9. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40106157 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics and Proteomics Integration in Neurological Syndromes.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2914:303-321. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4462-1_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40167926 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- #AF-939721/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- European Union's Horizon 2020
- R01AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG054047/Genomic and Metabolomic Data Integration in a Longitudinal Cohort at Risk for Alzheimer's Disease
- #ALFGBG-965240/ALF-agreement
- ZEN-21-848495/Alzheimer's Association 2021 Zenith Award
- #ADSF-21-831381-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037639/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG064877/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute
- #AF-930351/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #ALZ2022-0006/Hjärnfonden
- UL1TR000427/Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) program through the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- 1RF1AG074007/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- #FO2017-0243/Hjärnfonden
- R01AG021155/Longitudinal Course of Imaging Biomarkers in People at Risk of AD
- P41GM108538/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- Swedish Government and the County Councils
- #733050824736/Zon-MW, Redefining Alzheimer's disease
- UL1 TR000427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- #FO2019-0228/Hjärnfonden
- U01 AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #73305095005/ZONMW_/ZonMw/Netherlands
- #73305095005/Zon-MW, NCDC
- R01AG037639/White Matter Degeneration: Biomarkers in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease
- R01AG27161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #2017-00915/Swedish Research Council
- #201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- RF1 AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #733050824/ZonMW Memorabel grant programma
- P2CHD047873/University of Wisconsin-Madison
- AF-930934/Alzheimerfonden
- T32AG000213/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG064614/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- #ALFGBG-720931/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- #101053962/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG017266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #2018-02532/Swedish Research Council
- #SGT2021-09-Zetterberg/Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor
- 101034344/European Commission
- RF1 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG062715/Wisconsin Alzheimer's Disease Research Center Grant
- 115952/European Commission
- R01 AG027161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054047/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG017266/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG067092/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG033514/Wisconsin Alzheimer's Disease Research Center Grant
- RF1AG053303/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG062715/Wisconsin Alzheimer's Disease Research Center
- P30AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 860197/Marie Skłodowska-Curie
- #ADSF-21-831377-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- #EP2019-02/Erling-Persson Family Foundation
- RF1 AG074007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000213/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #115372/Innovative Medicines Inititiative Joint Undertaking under the EMIF
- R01AG021155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 806999/European Commission
- R01AG054047/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #ALFGBG-715986/ALF-agreement
- R01AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #ADSF-21-831376-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- R01AG27161/Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer Prevention: Biomarkers of Preclinical AD
- #AF-968270/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #OT2016-101/Olav Thon Foundation
- R01 AG064614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM108538/National Center for Quantitative Biology of Complex Systems
- #115372/EMIF
- RF1AG058501/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- #AF-930934/Alzheimerfonden
- P2C HD047873/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000427/NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
- R01AG037639/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- #733050824/ZonMW Memorabel
- R21AG067092/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG044546/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 10510022110012/Memorabel fellowship (ZonMW)
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- #733050824736/ZONMW_/ZonMw/Netherlands
- Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI)
- Foundation of Gamla Tjänarinnor
- P01AG003991/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG066444/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM108538/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG067092/Identifying Metabolomic Risk Factors in Plasma and CSF for Alzheimer's Disease
- R01AG064877/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG033514/Wisconsin Alzheimer's Disease Research Center
- R01AG064614/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG033514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG058922/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 2019-AARF-643973/Alzheimer's Association Research Fellowship
- #JPND2021-00694/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska'Curie
- 10510022110012/ZonMW Memorabel
- 1RF1AG074007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

