The multiple roles of nerve biopsy in the diagnosis and prognosis of suspected immune neuropathies
- PMID: 38811396
- PMCID: PMC11319532
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-024-12456-4
The multiple roles of nerve biopsy in the diagnosis and prognosis of suspected immune neuropathies
Abstract
Introduction: The value of a sural nerve biopsy for the diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) is controversial. Evidence-based recommendations for its implementation are lacking. We investigated factors leading to biopsy and analyzed biopsy outcomes and consequences, assessed the predictability of biopsy outcomes through clinical parameters to avoid unnecessary biopsies, and compared results with electrophysiological and clinical severity to determine their prognostic value.
Methods: 190 sural nerve biopsies were analyzed in two cohorts. One consisted of 163 biopsies and the second of 72 biopsies from the prospective Immune-mediated Neuropathies Biomaterial and Data registry (INHIBIT). Both have an intersection of 45 patients. 75 data sets from patients without biopsy were used. Analysis of nerve conduction studies, treatment, overall disability sum score (ODSS), biopsy outcomes, and diagnosis was performed.
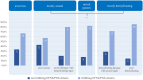
Results: 51% of biopsied patients received the diagnosis CIDP (77% fulfilled EFNS/PNS criteria), 21% were not CIDP typical, and 27% were unspecific. Biopsied patients responded less frequently to immunotherapies at time of biopsy than non-biopsied patients (p = 0.003). Immunotherapy was initiated more frequently after biopsy (p < 0.001) and more often with intravenous immunoglobulins (p < 0.0001). 76% of all biopsied patients met the electrophysiological criteria for CIDP. Sensory nerve action potential amplitudes of 0 µV still provide 73% of histological diagnostic value. Histologic signs of degeneration predicted ODSS worsening after 1 year (p = 0.028) but disease severity did not correlate with histological damage severity.
Discussion: The main indication for nerve biopsy was the treatment of refractory cases of autoimmune neuropathies with the therapeutic consequence of treatment initiation or escalation. Sural biopsy also provided prognostic information. Even with extinguished sural SNAP, the biopsy can still have diagnostic value.
Keywords: CIDP; Histology; Nerve biopsy; Polyneuropathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Rafael Klimas: received research funding from The LFB Group France and Ruhr-University, Bochum and travel funding from Grifols and Takeda; not related to this work. Anna Kordes, Sophie Huckemann, Zornitsa Gash, Joerg Phillips, Melissa Sgodzai, Thomas Grüter, Melis Sevindik, Christiane Schneider-Gold: no disclosures relevant to the article. Ralf Gold: serves on scientific advisory boards for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Biogen Idec, Bayer Schering Pharma, and Novartis; has received speaker honoraria from Biogen Idec, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Bayer Schering Pharma, and Novartis; serves as editor for Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Diseases and on the editorial boards of Experimental Neurology and the Journal of Neuroimmunology; and receives research support from Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Biogen Idec, Bayer Schering Pharma, Genzyme, Merck Serono, and Novartis, none related to this manuscript. Kathy Keyvani: no disclosures relevant to the article. Min-Suk Yoon has received speaker honoraria from CSL Behring and Grifols, a scientific grant from CSL Behring, none related to this manuscript. Anna Lena Fisse: received research funding by Georgius Agricola Stiftung Ruhr and Ruhr-University, Bochum (FoRUM-program), received honoraria and travel grants from Novartis AG, Sanofi and Eisai GmbH, none related to this work. Owns shares of Fresenius SE & Co., Gilead Sciences, Medtronic PLC and Novartis AG. None related to this work. Kalliopi Pitarokoili: received travel funding and speaker honoraria from Biogen Idec, Novartis and Bayer Schering Pharma and funding from the Ruhr-University, Bochum (FORUM-Program), none related to this work. Jeremias Motte: received travel grants from Biogen idec, Novartis AG, Teva and Eisai GmbH, his research is funded by Klaus Tschira Foundation and Ruhr-University, Bochum (FoRUM-program); Hertie foundation; Biogen idec; Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG); none related to this work.
Figures





References
-
- van den Bergh PYK, Hadden RDM, Bouche P, Cornblath DR, Hahn A, Illa I, Koski CL, Léger J-M, Nobile-Orazio E, Pollard J, Sommer C, van Doorn PA et al (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society-first revision. Eur J Neurol 17:356–363 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02930.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

