GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes
- PMID: 38811543
- PMCID: PMC11137047
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06754-y
GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes
Abstract
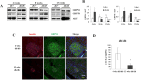
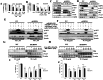
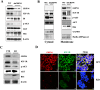
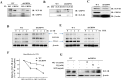
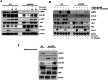
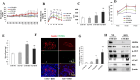
High workload-induced cellular stress can cause pancreatic islet β cell death and dysfunction, or β cell failure, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Thus, activation of molecular chaperones and other stress-response genes prevents β cell failure. To this end, we have shown that deletion of the glucose-regulated protein 94 (GRP94) in Pdx1+ pancreatic progenitor cells led to pancreas hypoplasia and reduced β cell mass during pancreas development in mice. Here, we show that GRP94 was involved in β cell adaption and compensation (or failure) in islets from leptin receptor-deficient (db/db) mice in an age-dependent manner. GRP94-deficient cells were more susceptible to cell death induced by various diabetogenic stress conditions. We also identified a new client of GRP94, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), a critical factor for β cell survival and function that may mediate the effect of GRP94 in the pathogenesis of diabetes. This study has identified essential functions of GRP94 in β cell failure related to diabetes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GRP94 is indispensable for definitive endoderm specification of human induced pluripotent stem cells.Mol Ther. 2025 Aug 6;33(8):3994-4006. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.04.025. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40254879
-
Hyperglycemia impairs EAAT2 glutamate transporter trafficking and glutamate clearance in islets of Langerhans: implications for type 2 diabetes pathogenesis and treatment.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):E27-E41. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00069.2024. Epub 2024 May 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38690938 Free PMC article.
-
Increased inflammation as well as decreased endoplasmic reticulum stress and translation differentiate pancreatic islets from donors with pre-symptomatic stage 1 type 1 diabetes and non-diabetic donors.Diabetologia. 2025 Jul;68(7):1463-1475. doi: 10.1007/s00125-025-06417-3. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 40457096 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections of insulin for pregnant women with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 7;2016(6):CD005542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27272351 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular puzzle of insulin: structural assembly pathways and their role in diabetes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 20;13:1502469. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1502469. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40052150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated N-glycosylation controls chaperone function and receptor trafficking.Science. 2024 Nov 8;386(6722):667-672. doi: 10.1126/science.adp7201. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Science. 2024. PMID: 39509507 Free PMC article.
-
The structural and functional dynamics of BiP and Grp94: opportunities for therapeutic discovery.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025 May;46(5):453-467. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2025.03.004. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40253284 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

