Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling coordinates adipose plasticity and energy balance by uncoupling leptin expression from fat mass
- PMID: 38811804
- PMCID: PMC11136666
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01045-4
Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling coordinates adipose plasticity and energy balance by uncoupling leptin expression from fat mass
Abstract
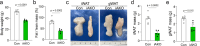
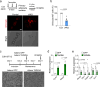
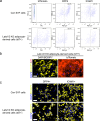
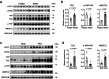
Adipose tissues serve as an energy reservoir and endocrine organ, yet the mechanisms that coordinate these functions remain elusive. Here, we show that the transcriptional coregulators, YAP and TAZ, uncouple fat mass from leptin levels and regulate adipocyte plasticity to maintain metabolic homeostasis. Activating YAP/TAZ signalling in adipocytes by deletion of the upstream regulators Lats1 and Lats2 results in a profound reduction in fat mass by converting mature adipocytes into delipidated progenitor-like cells, but does not cause lipodystrophy-related metabolic dysfunction, due to a paradoxical increase in circulating leptin levels. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that YAP/TAZ-TEAD signalling upregulates leptin expression by directly binding to an upstream enhancer site of the leptin gene. We further show that YAP/TAZ activity is associated with, and functionally required for, leptin regulation during fasting and refeeding. These results suggest that adipocyte Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling constitutes a nexus for coordinating adipose tissue lipid storage capacity and systemic energy balance through the regulation of adipocyte plasticity and leptin gene transcription.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.P. and I.-Y.K. hold equity in Myocare. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00218616/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00261586/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00218616/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C3005801/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C3005801/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C3005801/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00218616/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00218616/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- NRF-2020-2079551/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- RS-2023-00218616/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2021R1A2C2007573/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- ERC-AdG-787702/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- ERC-AdG-787702/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Excellent Science (H2020 Priority Excellent Science)
- ERC-AdG-787702/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Excellent Science (H2020 Priority Excellent Science)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

