A bistable inhibitory optoGPCR for multiplexed optogenetic control of neural circuits
- PMID: 38811857
- PMCID: PMC11239505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02285-8
A bistable inhibitory optoGPCR for multiplexed optogenetic control of neural circuits
Abstract
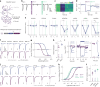
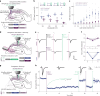
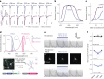
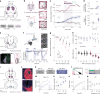
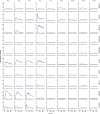
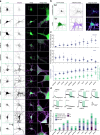
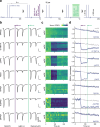
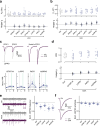
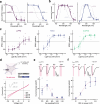
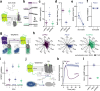
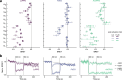
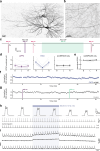
Information is transmitted between brain regions through the release of neurotransmitters from long-range projecting axons. Understanding how the activity of such long-range connections contributes to behavior requires efficient methods for reversibly manipulating their function. Chemogenetic and optogenetic tools, acting through endogenous G-protein-coupled receptor pathways, can be used to modulate synaptic transmission, but existing tools are limited in sensitivity, spatiotemporal precision or spectral multiplexing capabilities. Here we systematically evaluated multiple bistable opsins for optogenetic applications and found that the Platynereis dumerilii ciliary opsin (PdCO) is an efficient, versatile, light-activated bistable G-protein-coupled receptor that can suppress synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons with high temporal precision in vivo. PdCO has useful biophysical properties that enable spectral multiplexing with other optogenetic actuators and reporters. We demonstrate that PdCO can be used to conduct reversible loss-of-function experiments in long-range projections of behaving animals, thereby enabling detailed synapse-specific functional circuit mapping.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
O.Y. is listed as an inventor on a patent application (US20210403518A1) filed with the US Patent Office regarding type II bistable opsins and serves as a consultant for Modulight.bio. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
A bistable inhibitory OptoGPCR for multiplexed optogenetic control of neural circuits.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 2:2023.07.01.547328. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.01.547328. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2024 Jul;21(7):1275-1287. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02285-8. PMID: 37425961 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ERC-2016-StG 714762/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- ERC CoG 819496/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- H2020-RIA DEEPER 101016787/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- U01 NS128537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- SFB 1315/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- ALTF 378-2019/European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO)
- EXC-2049 - 390688087, SPP 1665, SFB 958/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SyG BrainPlay 810580/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- SPP1926/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 1U01NS128537-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Office of Extramural Research, National Institutes of Health (OER)
- SPP 1926/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- ERC-2019-CoG 864353/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- ERC-2019-STG 850784/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- ISF 1557/2/Israel Science Foundation (ISF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

