Applying LASSO logistic regression for the prediction of biliary complications after ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation in patients with end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis
- PMID: 38812045
- PMCID: PMC11134669
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-01898-1
Applying LASSO logistic regression for the prediction of biliary complications after ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation in patients with end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to explore the relevant risk factors associated with biliary complications (BCs) in patients with end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (HAE) following ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation (ELRA) and to establish and visualize a nomogram model.
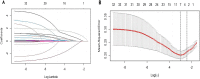
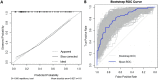
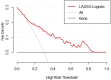
Methods: This study retrospectively analysed patients with end-stage HAE who received ELRA treatment at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University between August 1, 2010 and May 10, 2023. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression model was applied to optimize the feature variables for predicting the incidence of BCs following ELRA. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to develop a prognostic model by incorporating the selected feature variables from the LASSO regression model. The predictive ability, discrimination, consistency with the actual risk, and clinical utility of the candidate prediction model were evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration plots, and decision curve analysis (DCA). Internal validation was performed by the bootstrapping method.
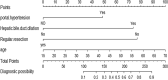
Results: The candidate prediction nomogram included predictors such as age, hepatic bile duct dilation, portal hypertension, and regular resection based on hepatic segments. The model demonstrated good discrimination ability and a satisfactory calibration curve, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.818 (95% CI 0.7417-0.8958). According to DCA, this prediction model can predict the risk of BCs occurrence within a probability threshold range of 9% to 85% to achieve clinical net benefit.
Conclusions: A prognostic nomogram with good discriminative ability and high accuracy was developed and validated to predict BCs after ELRA in patients with end-stage HAE.
Keywords: Biliary complications; Ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation; Hepatectomy; Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis; Liver transplantation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Sarcopenia-Based Prediction Model for Postoperative Complications of ex vivo Liver Resection and Autotransplantation to Treat End-Stage Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Nov 23;14:4887-4901. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S340478. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34848980 Free PMC article.
-
Application of ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation in treating Budd-Chiari syndrome secondary to end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: A case series.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 27;100(34):e27075. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027075. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34449508 Free PMC article.
-
Ex vivo liver resection and autotransplantation as alternative to allotransplantation for end-stage hepatic alveolar echinococcosis.J Hepatol. 2018 Nov;69(5):1037-1046. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30031886
-
Massive sympathetic nerve infiltration in advanced hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 May 23;22(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07470-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35606711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Particular Chinese contributions to extracorporeal liver surgery.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2025 Feb;24(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2024.12.005. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2025. PMID: 39753427 Review.
Cited by
-
The value of nomogram analysis in predicting pulmonary metastasis in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis.Sci Rep. 2025 May 14;15(1):16685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97134-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40369021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li T, Chen X, Zhen R, Qiu J, Qiu D, Xiao N, Ito A, Wang H, Giraudoux P, Sako Y, et al. Widespread coco-endemicity of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, northwest Sichuan/southeast Qinghai, China. Acta Trop. 2010;113(3):248–256. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.11.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

