The prognostic implications and tumor-promoting functions of CHSY3 in gastric cancer
- PMID: 38812506
- PMCID: PMC11133601
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1364979
The prognostic implications and tumor-promoting functions of CHSY3 in gastric cancer
Abstract
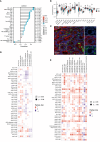
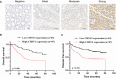
Chondroitin sulfate synthase 3 (CHSY3) is an important enzyme that regulates glycosylation, but its role in tumors has not been determined. Here, we showed that high CHSY3 expression promotes proliferation in gastric cancer (GC) cells and is associated with poor prognosis in GC patients. We analyzed the immunohistochemistry data of 150 gastric cancer patients to determine the clinicopathological and survival significance of CHSY3. Immunofluorescence was used to detect the colocalization of CHSY3 with infiltrating immune cells. Additionally, CHSY3 was predominantly found in tumor tissues and showed higher abundance compared to matched adjacent tissues. High CHSY3 expression was associated with more advanced tumor stage, higher recurrence risk and worse survival. Immunohistochemistry and bioinformatic analysis revealed that CHSY3 expression was significantly positively correlated with tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) infiltration. Moreover, after knocking down CHSY3, the proliferation of cells was decreased, and the migration ability was reduced, as shown by scratch, monoclonal and transwell assays. In conclusion, this study revealed that CHSY3 has a tumor-promoting effect on GC, suggesting a novel therapeutic strategy against this disease.
Keywords: CHSY3; gastric cancer; prognosis; tumor immune microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Zhang, Wei, Chen, Zheng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CHSY3 promotes proliferation and migration in gastric cancer and is associated with immune infiltration.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 17;21(1):474. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04333-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37461041 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated TUBA1A Might Indicate the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Gastric Cancer, Being Associated with the Infiltration of Macrophages in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020 Dec 12;29(4):509-522. doi: 10.15403/jgld-2834. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 33331338
-
Cuproptosis-related gene DLAT is a biomarker of the prognosis and immune microenvironment of gastric cancer and affects the invasion and migration of cells.Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(14):e70012. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70012. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39031012 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of HECW1 is associated with the poor prognosis and cancer progression of gastric cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 May 29;23(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03866-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40442732 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of glycometabolism-related genes reveals PLOD2 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Apr 15;25(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03878-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40229676 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A review shows that ATG10 has been identified as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target for cancer patients based on real-world studies.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 17;15:1573378. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1573378. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40313244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yuan Z, Cui H, Xu Q, Gao J, Liang W, Cao B, et al. . Total versus proximal gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a multicenter retrospective propensity score-matched cohort study. Int J Surg. (2023) 110(2):1000–7. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000927 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

