Immune responses during COVID-19 breakthrough cases in vaccinated children and adolescents
- PMID: 38812507
- PMCID: PMC11133585
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1372193
Immune responses during COVID-19 breakthrough cases in vaccinated children and adolescents
Abstract
Background: Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection has been somewhat limited due to the widespread dissemination of the Omicron variant, its subvariants, and the immune response dynamics of the naturally infected with the virus.
Methods: Twelve subjects between 3-17 years old (yo), vaccinated with two doses of CoronaVac®, were followed and diagnosed as breakthrough cases starting 14 days after receiving the second dose. Total IgGs against different SARS-CoV-2 proteins and the neutralizing capacity of these antibodies after infection were measured in plasma. The activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was evaluated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with peptides derived from the proteins from the wild-type (WT) virus and Omicron subvariants by flow cytometry, as well as different cytokines secretion by a Multiplex assay.
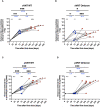
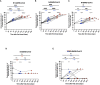
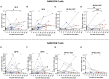
Results: 2 to 8 weeks post-infection, compared to 4 weeks after 2nd dose of vaccine, there was a 146.5-fold increase in neutralizing antibody titers against Omicron and a 38.7-fold increase against WT SARS-CoV-2. Subjects showed an increase in total IgG levels against the S1, N, M, and NSP8 proteins of the WT virus. Activated CD4+ T cells showed a significant increase in response to the BA.2 subvariant (p<0.001). Finally, the secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ cytokines showed a discreet decrease trend after infection in some subjects.
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 infection in the pediatric population vaccinated with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine produced an increase in neutralizing antibodies against Omicron and increased specific IgG antibodies for different SARS-CoV-2 proteins. CD4+ T cell activation was also increased, suggesting a conserved cellular response against the Omicron subvariants, whereas Th1-type cytokine secretion tended to decrease.
Clinical trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov #NCT04992260.
Keywords: CoronaVac®; SARS-CoV-2; breakthrough cases; inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; omicron variant; pediatric; phase 3 clinical trial.
Copyright © 2024 Rivera-Pérez, Méndez, Diethelm-Varela, Melo-González, Vázquez, Meng, Xin, Fasce, Fernández, Mora, Ramirez, Acevedo, Valiente-Echeverría, Soto-Rifo, Grifoni, Weiskopf, Sette, Astudillo, Le Corre, Abarca, Perret, González, Soto, Bueno and Kalergis.
Conflict of interest statement
XM and QX are SINOVAC Biotech employees, contributed to the conceptualization of the study, and did not participate in the analysis or interpretation of the data presented in the manuscript. AS is a consultant for AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, Calyptus Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Darwin Health, EmerVax, EUROIMMUN, F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd, Fortress Biotech, Gilead Sciences, Granite bio., Gritstone Oncology, Guggenheim Securities, Moderna, Pfizer, RiverVest Venture Partners, and Turnstone Biologics. AG is a consultant for Pfizer and Sanofi. La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) has filed for patent protection for various aspects of T cell epitope and vaccine design work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
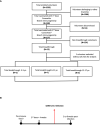
Similar articles
-
Neutralizing Activity and T-Cell Responses Against Wild Type SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Omicron BA.5 Variant After Ancestral SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Booster Dose in PLWH Receiving ART Based on CD4 T-Cell Count.J Korean Med Sci. 2025 Mar 10;40(9):e28. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e28. J Korean Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40065712 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Profile and Clinical Outcome of Breakthrough Cases After Vaccination With an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 29;12:742914. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.742914. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34659237 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neutralizing antibody response to Omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.5 in children and adolescents following the two-dose CoronaVac protocol (Immunita-002, Brazil): a 12-month longitudinal study.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1589733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589733. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40735326 Free PMC article.
-
Does the COVID-19 Vaccination Reduce the Risk to Transmit SARS-CoV-2 to Others?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1457:247-264. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-61939-7_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39283431 Review.
-
Neutralizing antibodies in milk and blood of lactating women vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2024 Sep 6;43:e2023210. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2025/43/2023210. eCollection 2024. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39258663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed 18 Dec2022).
-
- Mathieu E, Ritchie H, Rodés-Guirao L, Appel C, Giattino C, Hasell J, et al. . Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data; (2020). Available at: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus.
-
- Dembiński Ł, Vieira Martins M, Huss G, Grossman Z, Barak S, Magendie C, et al. . SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in children and adolescents—A joint statement of the european academy of pediatrics and the european confederation for primary care pediatricians. Front Pediatr. (2021) 9:721257. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.721257 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

