Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults and adolescents: epidemiology, diagnostic challenges, and management strategies for a type 2 inflammatory disease
- PMID: 38812705
- PMCID: PMC11135112
- DOI: 10.1177/17562848241249570
Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults and adolescents: epidemiology, diagnostic challenges, and management strategies for a type 2 inflammatory disease
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is recognized as a chronic type 2 inflammatory disease characterized by the eosinophilic infiltration of the esophageal tissue, posing a significant disease burden and highlighting the necessity for novel management strategies to address unmet clinical needs.
Objectives: To critically evaluate the existing literature on the epidemiology and management of EoE, identify evidence gaps, and assess the efficacy of current and emerging treatment modalities.
Design: An extensive literature review was conducted, focusing on the epidemiological trends, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic interventions for EoE. This was complemented by a survey among physicians and consultations with a scientific expert panel, including a patient's association (ESEO Italia), to enrich the study findings.
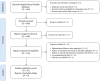
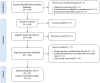
Data sources and methods: The review followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, scrutinizing epidemiological studies and management research to compile comprehensive insights into the disease's landscape. The physician survey and expert panel discussions aimed to bridge identified evidence gaps.
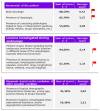
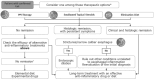
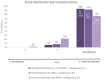
Results: The review included 59 epidemiological and 51 management studies, uncovering variable incidence and prevalence rates of EoE globally, with an estimated diagnosed prevalence of 41 per 100,000 in Italy. Diagnostic challenges were identified, including nonspecific symptoms and the lack of definitive biomarkers, which complicate the use of endoscopy. Treatment options such as elimination diets, proton-pump inhibitors, and swallowed corticosteroids were found to have varying success rates, while Dupilumab, an emerging therapy targeting interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13, shows promise.
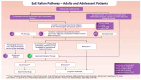
Conclusion: Despite advancements in understanding and managing EoE, significant unmet clinical needs remain, particularly in biomarker identification, therapy personalization, and cost-effectiveness evaluation. A comprehensive, multidimensional approach to patient management is required, emphasizing the importance of early symptom recognition, accurate diagnosis, and tailored treatment strategies. Dupilumab offers potential as a novel treatment, underscoring the need for future research to explore the economic and social dimensions of EoE care pathways.
Keywords: diagnosis; eosinophilic esophagitis; epidemiology; systematic review; treatment pathway.
Plain language summary
Understanding and improving care for eosinophilic esophagitis: bridging gaps in diagnosis and treatment Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the esophagus. We reviewed studies on how common EoE is and how it’s managed. In Italy, about 41 out of 100,000 people may have it. Diagnosis can be tricky due to vague symptoms, and current treatments vary in effectiveness. We found a need for better ways to diagnose and treat EoE, including exploring new therapies. A promising development is a biologic called Dupilumab. Future research should also consider the costs and social aspects of caring for people with EoE.
© The Author(s), 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
E.S. served as consultant for Abbvie, Agave, Alfasigma, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Diadema Farmaceutici, Dr. Falk, Fenix Pharma, Fresenius Kabi, Janssen, JB Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co, Nestlè, Reckitt Benckiser, Regeneron, Sanofi, SILA, Sofar, Synformulas GmbH, Takeda, and Unifarco; he received research support from Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, SILA, Sofar, Unifarco, and Zeta Farmaceutici. G.B. received consulting fees for analysis, conduction, and/or participation in Advisory Boards and/or Conferences from Aboca, AB Biotics, Agave, Alfasigma, AG Pharma, Bayer, Bromatech, Cadigroup, Biocodex, Sanofy, GE Healthcare, Mayoly, Diadema, and Sofar. M.B.B. received fees for lectures from ALK, Astra, Chiesi, GSK, and Sanofi. Nicola De Bortoli received consulting fee from Sofar, Reckitt-Benkiser, Dr. Falk, Malesci, Alfasigma, and Sanofi Genzyme; and for the participation to Advisory Board: Astra Zeneca, Dr. Falk. A.D.S. no conflict of interest to declare. S.O. received consulting fees from Sanofi, Alfasigma, Medtronic, and Bristol Myers Squibb. R.P. received consulting fees from Dr Falk Pharma and Sanofi for analysis conduction, or for the participation in Advisory Boards and/or Conferences. F.R. received consulting fees from Sanofi, Dr. Falk, GSK (Advisory Boards and Conferences). A.T. no conflict of interest to declare. F.R. no conflict of interest to declare. A.C. no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Botan V, Dos Santos Borges TK, Rocha Alves ÈA, et al.. Enhanced activation of eosinophils in peripheral blood and implications for eosinophilic esophagitis diagnosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 32: 1318–1327. - PubMed
-
- Chehade M, Kamboj AP, Atkins D, et al.. Diagnostic delay in patients with eosinophilic gastritis and/or duodenitis: a population-based study. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2021; 9: 2050.e20–2059.e20. - PubMed
-
- Khan S, Guo X, Liu T, et al.. An update on eosinophilic esophagitis: etiological factors, coexisting diseases, and complications. Digestion 2021; 102: 342–356. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

