Pathological Hip Dislocation in a Neurofibromatosis Patient Secondary to Capsular Hemangioma
- PMID: 38812877
- PMCID: PMC11130081
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-024-01166-8
Pathological Hip Dislocation in a Neurofibromatosis Patient Secondary to Capsular Hemangioma
Abstract
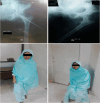
Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal-dominant multi-system disease affecting the nervous, integumentary, ocular, and musculoskeletal systems. In the small number of reported cases, the cause was either atraumatic or an intra-articular neurofibroma. Only a couple of articles in medical literature have reported synovial and capsular hemangioma originating within the hip joint. In this article, we present a rare case of pathological hip dislocation in a neurofibromatosis patient secondary to capsular hemangioma that would be reported for the first time in medical literature. We present the case of a 20-year-old female, resident of Karachi, who presented to the outpatient clinic with pain in the left hip join and inability to bear weight on left leg for 1 week. Diagnosed as a case of posterior hip dislocation after physical examination and imaging, her dislocation was reduced by the Allis method. This maneuver, however, was unsuccessful. Ultimately, the joint was reduced with open reduction via Steinmann pin because post-reduction hip joint was unstable to be contained into the acetabulum; therefore, Steinmann pin was used. The biopsy specimen taken from joint capsule and femoral neck during the surgery revealed cavernous hemangioma within the capsule. Hence, the etiology of posterior hip dislocation was attributed to the presence of capsular hemangioma within the hip joint. The surgery proved successful. The patient had remarkable recovery. The Steinmann pin was removed at 6 weeks, full weight-bearing started at 3 months, and range of motion extended from 0 to 90 degrees at 1 year with imaging studies showing a normally placed hip joint. The presented case reports an unusual etiology of a rare pathology occurring in association with a common genetic disease. It focuses on the importance of thorough examination and extensive relevant investigations in patients presenting with rare pathologies. These practices not only expedite the diagnosis and treatment of such patients, but can also reveal unusual etiologies responsible for uncommon pathologies. This case would help widen the differential diagnosis and treatment strategies of the physicians while dealing with neurofibromatosis patients with pathological hip dislocation. Level of Evidence This is a case report having Level of Evidence 4 in accordance with the levels developed by the Centre of Evidence Based Medicine (CEBM) for treatment.
Keywords: Cavernous hemangioma; Hip dislocation; Hip joint; Neurofibromatosis; Orthopedics.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surgical Hip Dislocation for the Treatment of Intra-Articular Injuries and Hip Instability Following Traumatic Posterior Dislocation in Children and Adolescents.J Pediatr Orthop. 2016 Oct-Nov;36(7):673-9. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000527. J Pediatr Orthop. 2016. PMID: 25985375
-
Inferior Hip Dislocation in a 60-Year-Old Man; a Case Report.Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2022 Feb 27;10(1):e17. doi: 10.22037/aaem.v10i1.1498. eCollection 2022. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35402998 Free PMC article.
-
[Hip dislocation following the treatment of femoral neck fracture--case report].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2010 Mar-Apr;138(3-4):248-51. doi: 10.2298/sarh1004248v. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2010. PMID: 20499511 Serbian.
-
Hip Dislocation and Subluxation in Athletes: A Systematic Review.Am J Sports Med. 2022 Aug;50(10):2834-2841. doi: 10.1177/03635465211036104. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Am J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34623933
-
Hip dislocation following minor trauma in a patient with neurofibromatosis type 1: a case report and review of the literature.Hip Int. 2015 Mar-Apr;25(2):188-90. doi: 10.5301/hipint.5000211. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Hip Int. 2015. PMID: 25768882 Review.
References
-
- Kumar R, Neto AD, Deavers MT, Amini B, Lewis VO. Spontaneous hip dislocation secondary to intraarticular neurofibroma: A case report. Skeletal radiology. 2014;43(7):1007–1011. - PubMed
-
- Lachiewicz PF, Salvati EA, Hely D, Ghelman B. Pathological dislocation of the hip in neurofibromatosis. A case report. JBJS. 1983;65(3):414–415. - PubMed
-
- Office of Neuroscience Communications and Engagement, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Neurofibromatosis Fact Sheet. Available from: https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-She... [Accessed 19 April 2021]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
