Retzius-sparing Robot-assisted Simple Prostatectomy: Perioperative and Short-term Functional Outcomes Assessed via Validated Questionnaires
- PMID: 38812921
- PMCID: PMC11134874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2024.05.002
Retzius-sparing Robot-assisted Simple Prostatectomy: Perioperative and Short-term Functional Outcomes Assessed via Validated Questionnaires
Abstract
Background and objective: Several surgical procedures have been reported for treatment of male patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to large benign outlet obstruction (BOO). The diffusion of robotic surgery offers the possibility to perform open simple prostatectomy (SP) with a minimally-invasive approach. Our aim was to report outcomes of the Retzius-sparing robot-assisted SP (RS-RASP) technique.
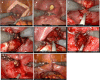
Methods: This was a single centre, prospective study. Patients with LUTS secondary to BOO and a prostate volume of >100 ml underwent RS-RASP performed with a da Vinci surgical system in four-arm configuration for a transperitoneal approach. Data for intraoperative and perioperative complications were collected. Functional outcomes were assessed via validated patient questionnaires. Univariable and multivariable regression analyses were used to identify predictors of complications and achievement of a trifecta composite outcome.
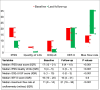
Key findings and limitations: The median patient age was 69 yr and the median prostate volume was 150 ml. The median operative time was 175 min, with estimated blood loss of 350 ml. The median in-hospital stay and median catheterisation time were 3 d and 9 d, respectively. Within 90 d, the incidence of complications was 3% for grade 1, 19% for grade 2, and 2% for grade 3 complications. At 7-mo follow-up, statistically significant improvements in International Prostate Symptom Scores (total score and quality of life), International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Urinary Incontinence Short Form (ICIQ-UI SF) scores, and the maximum flow rate were observed (all p < 0.0001). According to ICIQ-UI SF scores, 20%, 6%, and 3% of the patients had slight, moderate, or severe urinary incontinence (UI), respectively. Urgency UI was experienced by 14% of the patients and stress UI by 10%. Most of the patients with UI reported leakage of a small amount of urine and they did not wear pads.
Conclusions: RS-RASP was associated with good perioperative outcomes and a low prevalence of high-grade complications. Significant LUTS relief was achieved, but some patients experienced slight urgency or stress UI at short-term follow-up.
Patient summary: We explored a surgical technique called Retzius-sparing robot-assisted simple prostatectomy to treat men with bothersome urinary symptoms caused by a large prostate. The technique led to good results, with minimal bleeding and few complications during surgery. This surgery could be a beneficial choice for patients with stubborn urinary symptoms and a large prostate gland.
Keywords: Benign outlet obstruction; Complications; Continence; Lower urinary tract symptoms; Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy; Robotic surgery; Simple prostatectomy.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic enlargement: surgical technique and outcomes in a high-volume robotic centre.Eur Urol. 2015 Sep;68(3):451-7. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25887786
-
Retzius-sparing Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy Leads to Durable Improvement in Urinary Function and Quality of Life Versus Standard Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy Without Compromise on Oncologic Efficacy: Single-surgeon Series and Step-by-step Guide.Eur Urol. 2021 Jun;79(6):839-857. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 32536488
-
A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial Examining the Impact of the Retzius-sparing Approach on Early Urinary Continence Recovery After Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):677-685. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.04.029. Epub 2017 May 6. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28483330 Clinical Trial.
-
Retzius-sparing versus standard robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 18;8(8):CD013641. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013641.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32813279 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical treatment for urinary incontinence in women - Danish nationwide cohort studies .Dan Med J. 2018 Feb;65(2):B5447. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29393041 Review.
References
-
- Gravas S., Gacci M., Gratzke C., et al. Summary paper on the 2023 European Association of Urology guidelines on the management of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms. Eur Urol. 2023;84:207–222. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfo S.D., Del Giudice F., Chung B.I., et al. Robotic assisted simple prostatectomy versus other treatment modalities for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 6500 cases. Prostate Cancer Prostat Dis. 2023;26:495–510. doi: 10.1038/s41391-022-00616-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li K.P., Chen S.Y., Yang L. Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy versus robot-assisted simple prostatectomy for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative trials. J Robot Surg. 2023;17:351–364. - PubMed
-
- Kowalewski K.F., Hartung F.O., von Hardenberg J., et al. Robot-assisted simple prostatectomy vs endoscopic enucleation of the prostate: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative trials. J Endourol. 2022;36:1018–1028. - PubMed
-
- Grobet-Jeandin E., Pinar U., Rouprêt M. The place of robotic-assisted laparoscopy for BPO surgical management in 2021. Curr Opin Urol. 2021;31:438–443. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

