Genome-wide identification analysis in wild-type Solanum pinnatisectum reveals some genes defending against Phytophthora infestans
- PMID: 38812971
- PMCID: PMC11134371
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1379784
Genome-wide identification analysis in wild-type Solanum pinnatisectum reveals some genes defending against Phytophthora infestans
Abstract
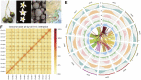
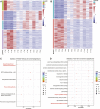
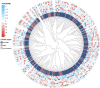
Solanum pinnatisectum exhibits strong resistance to late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans but only an incomplete genome assembly based on short Illumina reads has been published. In this study, we generated the first chromosome-level draft genome for the wild-type potato species S. pinnatisectum in China using Oxford Nanopore technology sequencing and Hi-C technology. The high-quality assembled genome size is 664 Mb with a scaffold N50 value of 49.17 Mb, of which 65.87% was occupied by repetitive sequences, and predominant long terminal repeats (42.51% of the entire genome). The genome of S. pinnatisectum was predicted to contain 34,245 genes, of which 99.34% were functionally annotated. Moreover, 303 NBS-coding disease resistance (R) genes were predicted in the S. pinnatisectum genome to investigate the potential mechanisms of resistance to late blight disease. The high-quality chromosome-level reference genome of S. pinnatisectum is expected to provide potential valuable resources for intensively and effectively investigating molecular breeding and genetic research in the future.
Keywords: Hi-C technology; assembly; ont; potatoes; resistance gene.
Copyright © 2024 Shen, Lu, Yang, Zhang, Huang, Li, Que and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors XZ and XH are employed by Grandomics Biosciences, Wuhan, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

