MicroRNA as a promising molecular biomarker in the diagnosis of breast cancer
- PMID: 38813102
- PMCID: PMC11134088
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1337706
MicroRNA as a promising molecular biomarker in the diagnosis of breast cancer
Abstract
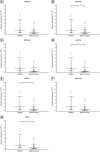
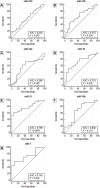
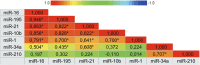
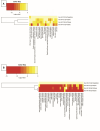
Introduction: Breast cancer represents the most prevalent malignancy among women. Recent advancements in translational research have focused on the identification of novel biomarkers capable of providing valuable insights into patient outcomes. Furthermore, comprehensive investigations aimed at discovering novel miRNAs, unraveling their biological functions, and deciphering their target genes have significantly contributed to our understanding of the roles miRNAs play in tumorigenesis. Consequently, these investigations have facilitated the way for the development of miRNA-based approaches for breast cancer prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment. However, conducting a more extensive array of studies, particularly among diverse ethnic groups, is imperative to expand the scope of research and validate the significance of miRNAs. This study aimed to assess the expression patterns of circulating miRNAs in plasma as a prospective biomarker for breast cancer patients within a population primarily consisting of individuals from Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC) communities. Methods: We evaluated 49 patients with breast cancer compared to 44 healthy women. Results and discussion: All miRNAs analyzed in the plasma of patients with breast cancer were downregulated. ROC curve analysis of miR-21 (AUC = 0.798, 95% CI: 0.682-0.914, p <0.0001), miR-1 (AUC = 0.742, 95% CI: 0.576-0.909, p = 0.004), miR-16 (AUC = 0.721, 95% CI: 0.581-0.861, p = 0.002) and miR-195 (AUC = 0.672, 95% CI: 0.553-0.792, p = 0.004) showed better diagnostic accuracy in discrimination of breast cancer patients in comparison with healthy women. miR-210, miR-21 showed the highest specificities values (97.3%, 94.1%, respectively). Following, miR-10b and miR-195 showed the highest sensitivity values (89.3%, and 77.8%, respectively). The panel with a combination of four miRNAs (miR-195 + miR-210 + miR-21 + miR-16) had an AUC of 0.898 (0.765-0.970), a sensitivity of 71.4%, and a specificity of 100.0%. Collectively, our results highlight the miRNA combination in panels drastically improves the results and showed high accuracy for the diagnosis of breast cancer displaying good sensitivity and specificity.
Keywords: cancer diagnosis; circulating miRNA; liquid biopsy; oncology; personalized medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Miranda, Slaibi-Filho, Calasans dos Santos, Carmo, Kaneto, Borin, Luiz and Gastalho Campos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma Circulating Mirnas Profiling for Identification of Potential Breast Cancer Early Detection Biomarkers.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 May 1;22(5):1375-1381. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1375. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34048164 Free PMC article.
-
Study on identification of a three-microRNA panel in serum for diagnosing neonatal early onset sepsis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023 Dec;36(2):2280527. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2023.2280527. Epub 2023 Nov 15. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023. PMID: 37968923
-
Diagnostic implication of a circulating serum-based three-microRNA signature in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 15;13:929787. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.929787. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36457743 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: a validation set from China.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Mar;94(10):e603. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000603. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25761179 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: New Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, Therapy Prediction and Therapeutic Tools for Breast Cancer.Theranostics. 2015 Jul 13;5(10):1122-43. doi: 10.7150/thno.11543. eCollection 2015. Theranostics. 2015. PMID: 26199650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The assessment of breast cancer biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment monitoring: integrated analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Aug 22;151(8):233. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06271-1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40844552 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Endocrine Modulators of Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 7;26(7):3449. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073449. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical implications of miR-195 in cancer: mechanisms, potential applications, and therapeutic strategies.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr 22;151(4):148. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06195-w. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40261408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brazil (2012). RESOLUTION No. 466, OF 12 DECEMBER 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

