A current era in pulsatile drug delivery system: Drug journey based on chronobiology
- PMID: 38813204
- PMCID: PMC11133509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29064
A current era in pulsatile drug delivery system: Drug journey based on chronobiology
Abstract
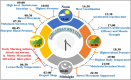
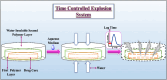
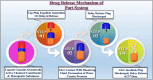
Almost all biological processes in the human body are regulated by circadian rhythm, which results in drastically different biochemical and physiological conditions throughout a 24 h period. Hence, suitable drug delivery systems should be efficiently monitored to attain the required therapeutic plasma concentration and therapeutic drug responses when needed as per chrono pharmacological concepts. "Chronotherapy" is the fast and transient release of a particular quantity of drug substance post a predetermined off-release period, termed as 'lag time'. Due to rhythmic variations, it is typically unnecessary to administer a medicine drug in an unhealthy condition constantly. Pulsatile drug delivery systems have received a lot of attention in pharmaceutical development because they give a quick or rate-controlled drug release after administration, followed by an anticipated lag period. Patients with various illnesses, such as asthma, hypertension, joint inflammation, and ulcers, can benefit from a pulsatile drug delivery system. Thus, a pulsatile drug delivery system may be a potential system for managing different diseases. This review mainly focuses on pulsatile drug delivery systems. It reviews and discusses the rationale, drug release mechanism, need, and system classification. In addition, it covers mainly externally regulated pulsatile drug delivery systems and recent advances in pulsatile systems like artificial intelligence and 3D printing. It also covers the ethical issues associated with pulsatile drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Dosing time; Extended time frame; Novel dosage forms; Pulsatile drug delivery; Release period.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Dickson M., Gagnon J.P. Key factors in the rising cost of new drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3(5):417–429. - PubMed
-
- Mullard A. New drugs cost US $2.6 billion to develop. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014;13(12):877.
-
- Yun Y., Lee B.K., Park K. Controlled drug delivery systems: the next 30 years. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2014;8(3):276–279. 2014/09/01.
-
- Ricotti L., Cafarelli A., Iacovacci V., et al. Advanced micro-nano-bio systems for future targeted therapies. Curr. Nanosci. 2015;11(2):144–160.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources