A disease warranting attention from neurosurgeons: primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
- PMID: 38813246
- PMCID: PMC11133574
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1392691
A disease warranting attention from neurosurgeons: primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
Abstract
Background: Primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PCNS-PTLD) is a rare condition, posing diagnostic and treatment challenges, with histological biopsy essential for diagnosis. Standardized treatment protocols are lacking. This disease requires urgent attention due to the increasing number of organ transplant surgeries and the use of immunosuppressive agents.
Methods: From 2020 to 2023, our center diagnosed five patients with PCNS-PTLD. We reviewed their clinical records and conducted a comprehensive analysis of 22 literatures on PCNS-PTLD cases following renal transplantation or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
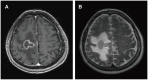
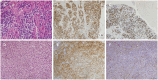
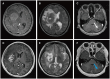
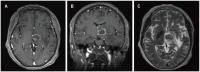
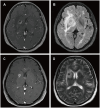
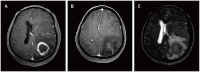
Results: Four patients had previously received a kidney transplant, one had undergone allogeneic HSCT. The median time from the last transplant surgery to the diagnosis of PCNS-PTLD differs between kidney transplant (21.5 years) and allogeneic HSCT (9 months). Common symptoms included motor weakness (n = 4), headache (n = 2), confusion (n = 2), and nausea (n = 2), with ring-enhancing (n = 5), typically solitary (n = 3) and supratentorial (n = 3) lesions on imaging. Diagnosis involved robot-assisted stereotactic brain biopsy (n = 4) or craniotomy (n = 1), all showing Epstein-Barr virus and CD20 positivity. Most cases (n = 4) were monomorphic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Treatment included rituximab (n = 3), surgical resection (n = 2), zanubrutinib (n = 1), whole-brain radiation (n = 1), and methotrexate (n = 1). At the last follow-up, the median duration of follow-up for all patients was 19 months. During this time, 3 patients had died and 2 patients were still alive.
Conclusion: In patients with a history of kidney transplantation or allogeneic HSCT who are on long-term immunosuppressive therapy, any neurological symptoms, particularly the presence of supratentorial ring-enhancing masses in the brain on imaging, whether solitary or multiple, should raise high suspicion for this disease, warranting a timely brain biopsy. Additionally, we found that besides reducing immunosuppressants, zanubrutinib may be a potential, safe, and effective treatment for this condition. Moreover, post-surgical administration of rituximab in conjunction with whole-brain radiotherapy also appears to be a potentially safe and effective approach.
Keywords: brain tumor; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; kidney transplant; primary central nervous system post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder; robot-assisted stereotactic brain biopsy.
Copyright © 2024 Jin, Lu, Yan, Han, Wei, Zhou, Wang, Shan and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer YL declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroimaging features of primary central nervous system post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder following hematopoietic stem cell transplant in patients with β-thalassemia: a case series and review of literature.Insights Imaging. 2024 Feb 14;15(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01605-y. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38353902 Free PMC article.
-
A case series of primary central nervous system posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder: imaging and clinical characteristics.Neurosurgery. 2013 Jun;72(6):960-70; discussion 970. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e31828cf619. Neurosurgery. 2013. PMID: 23685504 Free PMC article.
-
Primary CNS post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder following haploidentical HSCT using post-transplant high-dose cyclophosphamide.Blood Cell Ther. 2018 Oct 26;2(1):1-4. doi: 10.31547/bct-2018-004. eCollection 2019 Feb 25. Blood Cell Ther. 2018. PMID: 37969696 Free PMC article.
-
Effective management of primary central nervous system posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in a kidney transplant recipient using surgery and rituximab, along with a literature review.Transpl Immunol. 2025 May;90:102186. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2025.102186. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Transpl Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39892764 Review.
-
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder of the adrenal gland after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: report of two cases and literature review.Transpl Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;17(6):909-14. doi: 10.1111/tid.12461. Epub 2015 Nov 13. Transpl Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26426682 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

