Outcome of stress on G protein-coupled receptors and hypoxia inducible factor-1α
- PMID: 38813364
- PMCID: PMC11131643
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2023-0363
Outcome of stress on G protein-coupled receptors and hypoxia inducible factor-1α
Abstract
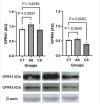
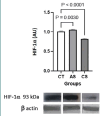
Stress drives neuroendocrine signals with detrimental effects to the intestinal homeostasis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of stress on intestinal hypoxia response elements, including G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41), GPR43, and hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α. Groups of five BALB/c mice were subjected to acute (2 h per day) and chronic (2 h per day for 4 days) stress induced by restraint, and the results were compared to those of an unstressed control group. Whole mucosal samples from the colon were collected to evaluate the expression of GPR41, GPR43 and HIF-1α using Western blot chemiluminescent analysis. Compared to the control group, in the chronic stress group the expression of GPR43 (P = 0.0092) and HIF-1α (P < 0.0001) were significantly lower and the expression of GPR41 was similar (P = 0.9184); acute stress significantly increased HIF-1α expression (P = 0.0030) and increased GPR41 expression (P = 0.0937), without affecting GPR43 (P = 0.9184). These findings offer insights into the modulation of hypoxia response elements under stress conditions and their pharmacological implications for developing drugs that mitigate the effects of stress on intestinal homeostasis.
Keywords: GPR41/GPR43; HIF-1α; colon; hypoxia; restraint stress.
© 2024 by the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α-induced interleukin-33 expression in intestinal epithelia contributes to mucosal homeostasis in inflammatory bowel disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Mar;187(3):428-440. doi: 10.1111/cei.12896. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27921309 Free PMC article.
-
Short-chain fatty acids activate GPR41 and GPR43 on intestinal epithelial cells to promote inflammatory responses in mice.Gastroenterology. 2013 Aug;145(2):396-406.e1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.056. Epub 2013 May 7. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23665276
-
Expression of short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR41 in the human colon.Biomed Res. 2009 Jun;30(3):149-56. doi: 10.2220/biomedres.30.149. Biomed Res. 2009. PMID: 19574715
-
Activation of HIF-1α does not increase intestinal tumorigenesis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;307(2):G187-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00112.2014. Epub 2014 May 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24875099 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of short-chain fatty acids receptors, GPR41 and GPR43 on colonic functions.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;59 Suppl 2:251-62. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18812643 Review.
References
-
- Brzozowski B, Mazur-Bialy A, Pajdo R, Kwiecien S, Bilski J, Zwolinska-Wcislo M, et al. Mechanisms by which Stress Affects the Experimental and Clinical Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Role of Brain-Gut Axis. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(8):892–900. doi: 10.2174/1570159x1466616040412412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
