Protective effects of safranal on kidney tissue in a rat model of distant ischemia-reperfusion injury with infrarenal aortic occlusion
- PMID: 38813504
- PMCID: PMC10760533
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0144.5726
Protective effects of safranal on kidney tissue in a rat model of distant ischemia-reperfusion injury with infrarenal aortic occlusion
Abstract
Background/aim: Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury to a part of the body can cause damage to distant organs such as the kidney and heart. This study investigated the protective effects of safranal against IR-induced renal injury.
Materials and methods: Used in this study were 24 Wistar Albino male rats, which were divided into 3 equal and randomised groups. The sham group underwent laparotomy only. In the IR group, the infrarenal aorta was clamped for 1 h, and then reperfused for 2 h. In the IR-safranal group, safranal was administered 30 min before the procedure and IR injury was induced in the same way as in the IR group. After the procedure, blood and tissue samples were collected from the rats for biochemical and histopathological analyses. Antioxidant capacity and proinflammatory cytokine analyses were performed on the blood samples. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining was performed to determine the number of cells undergoing apoptosis in the kidney tissue.
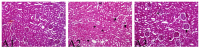
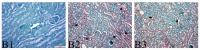
Results: The estimated glomerular filtration rate, an indicator of renal function, was lower in the IR group (p1 = 0.024 vs. p3 = 0.041, respectively) compared to the other groups, while creatinine levels were higher in the IR group compared to the other groups (p1 = 0.032 vs. p2 = 0.044, respectively). The blood urea nitrogen level was higher in the IR group than in the other groups (p1 = 0.001vs p2 = 0.035, respectively). The total antioxidant and total oxidant status, indicating tissue oxidative stress, did not differ between groups (p = 0.914 vs. p = 0.184, respectively). Among the proinflammatory cytokines, the interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the IR group (p = 0.034 vs. p = 0.001, respectively), but the tumour necrosis factor-α (p = 0.19), and interferon-γ (p = 0.311) levels did not differ between groups. Histopathological examination showed significantly less damage to glomerular and tubular cells in the IR-safranal group (p < 0.001). The number of TUNEL-positive cells was higher in the IR group compared to the other groups (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Safranal may have protective effects against kidney damage caused by distant ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Keywords: Infrarenal aortic occlusion; ischemia and reperfusion; renal injury; safranal.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no proprietary or commercial interest in any of the products mentioned or concepts discussed within the article. There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of the effect of safranal and crocin pre-treatment on hepatic injury induced by infrarenal aortic occlusion.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:160-166. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.06.027. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27470563
-
The effects of IL-18BP on mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines and apoptotic genes in renal injury induced by infrarenal aortic occlusion.J Surg Res. 2016 May 1;202(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.12.026. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27083945
-
Investigation of the effect of crocin pretreatment on renal injury induced by infrarenal aortic occlusion.J Surg Res. 2016 Jun 1;203(1):145-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.03.022. Epub 2016 Mar 19. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27338545
-
Antioxidant, Antiapoptotic and Inflammatory Effects of Interleukin-18 Binding Protein on Kidney Damage Induced by Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion.Am J Med Sci. 2016 Jun;351(6):607-15. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2016.02.017. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Am J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27238925
-
The Protective Effect of Adalimumab on Renal Injury in a Model of Abdominal Aorta Cross-Clamping.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2016 Mar-Apr;25(2):219-26. doi: 10.17219/acem/33250. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27627553
Cited by
-
Effects of 8-week Theracurmin Super (TS-P1; Curcumin) supplementation on exercise-induced oxidative stress: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel clinical trial.Integr Med Res. 2025 Mar;14(1):101099. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101099. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Integr Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39897573 Free PMC article.
-
Safranal Ameliorates Renal Damage, Inflammation, and Podocyte Injury in Membranous Nephropathy via SIRT/NF-κB Signalling.Curr Med Sci. 2025 Apr;45(2):288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11596-025-00020-8. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Curr Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sadeghnia HR, Kamkar M, Assadpour E, Boroushaki MT, Ghorbani A. Protective effect of safranal, a constituent of Crocus sativus, on quinolinic acid-induced oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences. 2013;16(1):73–82. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2013.251. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

