Analysis of imaging in pediatric bronchopulmonary foregut malformations with literature review: case reports
- PMID: 38813545
- PMCID: PMC11133687
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1400124
Analysis of imaging in pediatric bronchopulmonary foregut malformations with literature review: case reports
Abstract
Background: Bronchopulmonary foregut malformation (BPFM) is an uncommon condition, with few case reports documented in both national and international literature. This scarcity underscores the importance of utilizing effective imaging techniques to improve our understanding and diagnostic precision concerning this disorder.
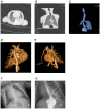
Case description: In the first case report, a neonate, born at full term and aged 15 days, presented with symptoms including dyspnea, coughing, wheezing, cyanosis, and vomiting. Initial diagnostic evaluations, which included chest radiography and upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, led to an erroneous initial diagnosis of a left-sided diaphragmatic hernia, accompanied by a suspicion of infection. In the second case report, another neonate, also born at full term but aged 5 days, exhibited symptoms such as coughing, choking, and mild vomiting. Utilizing a combination of computed tomography (CT) scans (plain, enhanced, and reconstructed), chest x-ray, and upper gastrointestinal tract radiography, the diagnosis of BPFM was accurately determined.
Conclusion: Comprehensive imaging examinations play a crucial role in reducing misdiagnosis and diagnostic oversights in cases of BPFM. Given its rarity, BPFM often manifests as a sequestered lung accompanied by gastrointestinal abnormalities. Hence, the integration of CT scans with gastrointestinal tract radiography can substantially improve diagnostic precision in such cases.
Keywords: CT; bronchopulmonary foregut malformation; pediatrics; sequestered lung; upper gastrointestinal tract radiography.
© 2024 Ji, Zhang, Guan, Song and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnosis and treatment of communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation: Report of two cases and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Mar;96(11):e6307. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006307. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28296740 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation including ectopic pancreatic tissue in an infant.Surg Case Rep. 2021 May 24;7(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s40792-021-01211-w. Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34028645 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical characteristics of bronchopulmonary foregut malformation].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 2;55(8):628-631. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2017.08.016. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28822441 Chinese.
-
Bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: embryology, radiology and quandary.Eur Radiol. 2003 Dec;13(12):2659-73. doi: 10.1007/s00330-002-1812-5. Epub 2003 Feb 12. Eur Radiol. 2003. PMID: 14631525 Review.
-
Bronchopulmonary and neurenteric forms of foregut anomalies. Imaging for diagnosis and management.Radiol Clin North Am. 1991 Mar;29(2):241-54. Radiol Clin North Am. 1991. PMID: 1998049 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

