Anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as potent mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: in vitro and in silico studies
- PMID: 38814149
- PMCID: PMC11141316
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2357174
Anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as potent mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: in vitro and in silico studies
Abstract
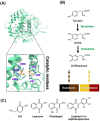
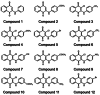
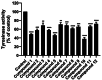
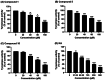
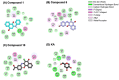
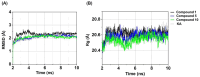
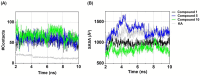
Tyrosinase, a pivotal enzyme in melanin synthesis, is a primary target for the development of depigmenting agents. In this work, in vitro and in silico techniques were employed to identify novel tyrosinase inhibitors from a set of 12 anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives. Results from the mushroom tyrosinase activity assay indicated that, among the 12 derivatives, three compounds (1, 5, and 10) demonstrated the most significant inhibitory activity against mushroom tyrosinase, surpassing the effectiveness of the kojic acid. Molecular docking revealed that all studied derivatives interacted with copper ions and amino acid residues at the enzyme active site. Molecular dynamics simulations provided insights into the stability of enzyme-inhibitor complexes, in which compounds 1, 5, and particularly 10 displayed greater stability, atomic contacts, and structural compactness than kojic acid. Drug likeness prediction further strengthens the potential of anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as promising candidates for the development of novel tyrosinase inhibitors for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.
Keywords: Tyrosinase inhibition; anilino-14-naphthoquinones; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of bis-thiourea derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: combined experimental and computational study.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025 Dec;40(1):2518195. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2518195. Epub 2025 Jun 24. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40556424
-
Synthesis, computational molecular docking analysis and effectiveness on tyrosinase inhibition of kojic acid derivatives.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Jul;88:102950. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.102950. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31075740
-
Novel Amide Derivatives as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors; In-vitro, In-vivo Antimelanogenic Activity and Computational Studies.Med Chem. 2019;15(7):715-728. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190319101329. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30892163
-
Azole inhibitors of mushroom and human tyrosinases: Current advances and prospects of drug development for melanogenic dermatological disorders.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 5;239:114525. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114525. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35717871 Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of paeonol thiosemicarbazone analogues as mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013 Nov;62:589-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.056. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013. PMID: 24120880 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the binding interaction of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivative-human serum albumin complex by biophysics and molecular simulation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 2;15(1):19249. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02787-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40456782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ismaya WT, Rozeboom HJ, Weijn A, Mes JJ, Fusetti F, Wichers HJ, Dijkstra BW.. Crystal structure of Agaricus bisporus mushroom tyrosinase: identity of the tetramer subunits and interaction with tropolone. Biochemistry. 2011;50(24):5477–5486. - PubMed
-
- Sansinenea E, Ortiz A.. Melanin: a photoprotection for Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(3):483–490. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
