Recent additions and access to a multidimensional lipidomic database containing liquid chromatography, ion mobility spectrometry, and tandem mass spectrometry information
- PMID: 38814344
- PMCID: PMC11427178
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-024-05351-4
Recent additions and access to a multidimensional lipidomic database containing liquid chromatography, ion mobility spectrometry, and tandem mass spectrometry information
Abstract
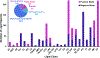
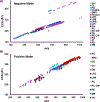
The importance of lipids in biology continues to grow with their recent linkages to more diseases and conditions, microbiome fluctuations, and environmental exposures. These associations have motivated researchers to evaluate lipidomic changes in numerous matrices and studies. Lipidomic analyses, however, present numerous challenges as lipid species have broad chemistries that require different extraction methods and instrumental analyses to evaluate and separate their many isomers and isobars. Increasing knowledge about different lipid characteristics is therefore crucial for improving their separation and identification. Here, we present a multidimensional database for lipids analyzed on a platform combining reversed-phase liquid chromatography, drift tube ion mobility spectrometry, collision-induced dissociation, and mass spectrometry (RPLC-DTIMS-CID-MS). This platform and the different separation characteristics it provides enables more confident lipid annotations when compared to traditional tandem mass spectrometry platforms, especially when analyzing highly isomeric molecules such as lipids. This database expands on our previous publication containing only human plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lipids and provides experimental RPLC retention times, IMS collision cross section (CCS) values, and m/z information for 877 unique lipids from additional biofluids and tissues. Specifically, the database contains 1504 precursor [M + H]+, [M + NH4]+, [M + Na]+, [M-H]-, [M-2H]2-, [M + HCOO]-, and [M + CH3COO]- ion species and their associated CID fragments which are commonly targeted in clinical and environmental studies, in addition to being present in the chloroform layer of Folch extractions. Furthermore, this multidimensional RPLC-DTIMS-CID-MS database spans 5 lipid categories (fatty acids, sterols, sphingolipids, glycerolipids, and glycerophospholipids) and 24 lipid classes. We have also created a webpage (tarheels.live/bakerlab/databases/) to enhance the accessibility of this resource which will be populated regularly with new lipids as we identify additional species and integrate novel standards.
Keywords: Collision cross section; Database; Ion mobility spectrometry; Lipidomics; Lipids; Mass spectrometry; Reverse phase liquid chromatography (RPLC).
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH, DE part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Confidence Shotgun Lipidomics Using Structurally Selective Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2306:11-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1410-5_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33954937 Free PMC article.
-
An Untargeted Lipidomics Workflow Incorporating High-Resolution Demultiplexing (HRdm) Drift Tube Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Oct 2;35(10):2448-2457. doi: 10.1021/jasms.4c00251. Epub 2024 Sep 14. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 39276100 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a liquid chromatography-ion mobility-high resolution mass spectrometry platform for untargeted lipidomics and application to HepaRG cell extracts.Talanta. 2021 Dec 1;235:122808. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122808. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 34517665
-
Utilizing Skyline to analyze lipidomics data containing liquid chromatography, ion mobility spectrometry and mass spectrometry dimensions.Nat Protoc. 2022 Nov;17(11):2415-2430. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00714-6. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35831612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating the potential of ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry in the separation and structural characterisation of lipid isomers.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Mar 16;10:1112521. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1112521. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37006618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multidimensional library for the improved identification of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).Sci Data. 2025 Jan 25;12(1):150. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04363-0. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39863618 Free PMC article.
-
Don't Be Surprised When These Surprise You: Some Infrequently Studied Sphingoid Bases, Metabolites, and Factors That Should Be Kept in Mind During Sphingolipidomic Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 14;26(2):650. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020650. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- LIPID MAPS® Structure Database (LMSD) [Available from: https://www.lipidmaps.org/databases/lmsd/overview]. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

