Acute skin toxicity and self-management ability among Chinese breast cancer radiotherapy patients: a qualitative study
- PMID: 38814489
- PMCID: PMC11139738
- DOI: 10.1007/s00520-024-08583-3
Acute skin toxicity and self-management ability among Chinese breast cancer radiotherapy patients: a qualitative study
Abstract
Objectives: Radiation dermatitis is the most common reaction to radiotherapy, almost all breast cancer patients receive radiotherapy on an outpatient basis. Currently, there are no studies on the experience of radiation dermatitis and the ability to self-manage it. Therefore, we aimed to use qualitative approaches to gain a deeper understanding of the actual experiences and self-management ability in order to provide a reference for further improving the effectiveness of self-management and to optimize symptom management strategies.
Methods: A descriptive qualitative study was conducted using purposive sampling to select 17 breast cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy. Semi-structured interviews were conducted from September to November 2023. The Colaizzi seven-step analysis method was used to classify the data into summarized themes.
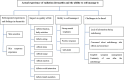
Results: Four themes were identified from the interview responses: (1) multiple self-reported skin symptoms in breast cancer patients with radiation dermatitis; (2) the multidimensional impact on patient's quality of life, especially pruritus, ulceration; (3) the ability to self-manage radiation dermatitis: strong mental toughness, positive response, and self-doubt; (4) challenges faced: concerns about radiotherapy side effects and recurrence, targeted symptom management and continuity of care after the radiotherapy.
Conclusions: Healthcare professionals should consider patients' self-reported symptoms when assessing radiation dermatitis. For pruritus and pain, we can enhance precision symptom management to improve patients' quality of life. By utilizing information technology tools, we can increase breast cancer patients' ability and confidence in managing radiation dermatitis effectively while enhancing accurate symptom management during radiotherapy.
Keywords: Breast neoplasm; Qualitative research; Quality of life; Radiodermatitis; Radiotherapy; Self-management.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Instruments to Evaluate Self-Management of Radiation Dermatitis in Patients With Breast Cancer.Oncol Nurs Forum. 2020 Jan 1;47(1):101-111. doi: 10.1188/20.ONF.101-111. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2020. PMID: 31845919
-
A qualitative analysis of acute skin toxicity among breast cancer radiotherapy patients.Psychooncology. 2011 Mar;20(3):260-8. doi: 10.1002/pon.1734. Psychooncology. 2011. PMID: 20238306 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-reported symptoms of radiation dermatitis during breast cancer radiotherapy: a pilot study.Qual Life Res. 2017 Jul;26(7):1713-1719. doi: 10.1007/s11136-017-1526-4. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Qual Life Res. 2017. PMID: 28238091
-
Randomized, Prospective, Open-label Phase III Trial Comparing Mebo Ointment With Biafine Cream for the Management of Acute Dermatitis During Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer.Am J Clin Oncol. 2018 Dec;41(12):1257-1262. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000460. Am J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29889137 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiation-induced Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Trials.Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Oct;18(5):e825-e840. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30072193
Cited by
-
Construction of a home-based self-management program for patients with indwelling peripherally inserted central catheter based on the IMB model.BMC Nurs. 2025 Apr 17;24(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03056-2. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40247325 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring health challenges and coping strategies in young patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: a qualitative study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 11;26(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04320-y. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40646455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378(9804):1707–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- EBCTCG (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group) McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9935):2127–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366(9503):2087–2106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical