The Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Renal Insufficiency
- PMID: 38814568
- PMCID: PMC11465476
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0072
The Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Renal Insufficiency
Abstract
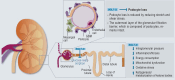
Background: Chronic renal insufficiency (CRI) is becoming more common and has an increasing impact on public health. In Germany, approximately one in ten adults has CRI. Its most serious consequence is generally not the development of end-stage renal failure, but rather the markedly increased cardiovascular risk as kidney function declines.
Methods: This review is based on the findings of a selective search in PubMed for literature about the treatment options for CRI, and on our overview of the existing guideline recommendations on diagnostic testing. .
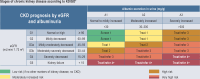
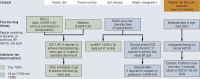
Results: Patients with diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension are at especially high risk of developing CRI. For these patients, some of the guidelines recommend regular testing for albuminuria and measurement of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), though sometimes only when specific risk constellations are present. The treatment of CRI has evolved in recent years. At first, aside from general measures, only RAS inhibitors were available as a specific therapy for CRI. With the extension of the approval of SGLT-2 inhibitors to non-diabetic CRI patients, the options for treatment have become wider. Two randomized controlled trials have revealed the benefit of SGLT-2 inhibitors with respect to their primary combined endpoints: time to a specified eGFR reduction and renal/cardiovascular death (HR 0.61 [0.51; 0.72] and 0.72 [0.64; 0.82]). The potential side effects and contraindications of SGLT-2 inhibitors must be taken into account. A further treatment option for diabetics with CRI has become available with the approval of the non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist finerenone.
Conclusion: In patients with risk factors, renal function should be regularly tested.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Finerenone and Heart Failure Outcomes by Kidney Function/Albuminuria in Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes.JACC Heart Fail. 2022 Nov;10(11):860-870. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2022.07.013. Epub 2022 Oct 12. JACC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 36328655 Clinical Trial.
-
Survival and long-term cardiovascular outcomes after carotid endarterectomy in patients with chronic renal insufficiency.Ann Vasc Surg. 2015 Jan;29(1):15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.07.029. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Ann Vasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 25194551
-
An analysis of DPV and DIVE registry patients with chronic kidney disease according to the finerenone phase III clinical trial selection criteria.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 May 8;22(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01840-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37158855 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on heart failure events in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2024 Jul 16;10(4):329-341. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvae003. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38218589
-
Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists and hyperkalemia monitoring in chronic kidney disease patients associated with type II diabetes: a narrative review.Postgrad Med. 2024 Mar;136(2):111-119. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2024.2316572. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 38344772 Review.
Cited by
-
In Reply.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024 Sep 6;121(18):618. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0162. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024. PMID: 39656624 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Malnutrition in Elderly Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-The Role of Albuminuria.Life (Basel). 2025 May 31;15(6):898. doi: 10.3390/life15060898. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566551 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of amino acid supplementation on renal function and nutritional parameters in patients with renal insufficiency: bibliometric analysis and meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 13;12:1594507. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1594507. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40584098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between serum methylmalonic acid and chronic kidney disease in adults: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2013-2014.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 1;15:1434299. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1434299. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39149121 Free PMC article.
-
Unfortunate Terminology.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024 Sep 6;121(18):618. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0161. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024. PMID: 39656623 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fioretto P, Pontremoli R. Expanding the therapy options for diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2022;18:78–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

