Impact of Physical Activity Frequency, Duration, and Intensity on Senile Cataract Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 38814746
- PMCID: PMC11146084
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.13.5.26
Impact of Physical Activity Frequency, Duration, and Intensity on Senile Cataract Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to determine the causal effects of physical activities with different frequencies, durations, and intensities on the risk of senile cataracts using Mendelian randomization (MR).
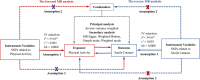
Methods: A bidirectional two-sample MR approach was used to determine the association between physical activity and senile cataract risk. Our primary analysis used the inverse variance weighted method, and secondary analyses included MR-Egger regression, MR-PRESSO, and Cochran's Q statistic to evaluate heterogeneity and pleiotropy. Causal estimates were presented as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
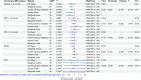
Results: Genetically predicted moderate physical activity ≥ 10 min/wk (OR = 0.765, 95% CI = 0.627-0.936, P = 8.73E-03), vigorous physical activity ≥ 10 min/wk (OR = 0.691, 95% CI = 0.521-0.917, P = 1.04E-02), moderate-to-vigorous physical activity levels (OR = 0.552, 95% CI = 0.369-0.823, P = 3.75E-03), and overall acceleration average (OR = 0.952, 95% CI = 0.926-0.978, P = 3.80E-04) were associated with a decreased risk of senile cataract while walking ≥ 10 min/wk (OR = 0.972, 95% CI = 0.741-1.275, P = 8.36E-01) had no significant correlation. The reverse MR analysis showed no reversal causality from senile cataract to physical activity except for walking ≥ 10 min/wk (OR = 0.951, 95% CI = 0.923-0.979, P = 7.30E-04).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that moderate to vigorous physical activity with higher frequency and longer duration will causally reduce the risk of senile cataracts, and there is no reverse causal relationship.
Translational relevance: These findings underscore the potential of incorporating physical activity into preventive health strategies for senile cataracts.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Multi-omics Mendelian randomization study on the causality between non-ionizing radiation and facial aging].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;41(6):594-603. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240830-00320. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40588408 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Inflammatory cytokines mediate the gut microbiota-EGPA subtype link: a Mendelian randomization study.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):3061-3071. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07526-5. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40500572
-
Ischemic Stroke May Increase the Risk of Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: Evidence from a Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study.World Neurosurg. 2025 Apr;196:123718. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2025.123718. Epub 2025 Mar 13. World Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 39929265
-
Exercise for intermittent claudication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 26;12(12):CD000990. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000990.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29278423 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Causal association between immunoglobulin G N-glycosylation patterns and diabetic complications: two-sample mendelian randomization.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Jul 18;17(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01858-7. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40682148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanito M. Reported evidence of vitamin E protection against cataract and glaucoma. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021; 177: 100–119. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2019 Blindness and Vision Impairment Collaborators; Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the Right to Sight: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021; 9(2): e144–e160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pascolini D, Mariotti SP.. Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012; 96(5): 614–618. - PubMed
-
- Flaxman SR, Bourne RRA, Resnikoff S, et al. .. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990-2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017; 5(12): e1221–e1234. - PubMed

