Violence and aggression against educators and school personnel, retention, stress, and training needs: National survey results
- PMID: 38815064
- PMCID: PMC11952076
- DOI: 10.1037/amp0001348
Violence and aggression against educators and school personnel, retention, stress, and training needs: National survey results
Abstract
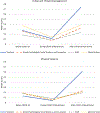
Aggression and violence against educators and school personnel have raised public health concerns that require attention from researchers, policymakers, and training providers in U.S. schools. School aggression and violence have negative effects on school personnel health and retention and on student achievement and development. In partnership with several national organizations, the American Psychological Association (APA) Task Force on Violence Against Educators and School Personnel administered two national, multi-informant, cross-sectional surveys. Time 1 data were collected in 2020-2021 from 14,966 respondents; participants reflected on their experiences of violence and aggression before COVID-19 and during COVID-19 restrictions in this survey. One year later, in 2022, 11,814 respondents completed the Time 2 survey after COVID-19 restrictions ended. Participants included teachers, school psychologists, social workers, counselors, staff members, and administrators from all 50 states and Puerto Rico. Rates of violence and aggression directed against educators by students, parents, colleagues, and administrators were substantial before COVID-19, were lower during COVID-19 restrictions, and returned to prepandemic levels or higher after COVID-19 restrictions. After COVID-19 restrictions, 22%-80% of respondents reported verbal or threatening aggression, and 2%-56% of respondents reported physical violence at least once during the year, varying by stakeholder role and aggressor. Rates of intentions to quit the profession ranged from 21% to 43% during COVID-19 restrictions (2020-2021) and from 23% to 57% after COVID-19 restrictions (2021-2022), varying by stakeholder role. Participants across roles reported substantial rates of anxiety and stress, especially during and after COVID-19 restrictions, and identified specific training needs. Implications for theory, research, training, and policy are presented. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2024 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures


References
-
- Amitai A, & Van Houtte M. (2022). Being pushed out of the career: Former teachers’ reasons for leaving the profession. Teaching and Teacher Education, 110, Article 103540. 10.1016/j.tate.2021.103540 - DOI
-
- Astor RA, & Benbenishty R. (2019). Bullying, school violence, and climate in evolving contexts: Culture, organization, and time. Oxford University Press.
-
- Bass BI, Cigularov KP, Chen PY, Henry KL, Tomazic RG, & Li Y. (2016). The effects of student violence against school employees on employee burnout and work engagement: The roles of perceived school unsafety and transformational leadership. International Journal of Stress Management, 23(3), 318–336. 10.1037/str0000011 - DOI
