Narrative review of occupational exposures and noncommunicable diseases
- PMID: 38815981
- PMCID: PMC11229329
- DOI: 10.1093/annweh/wxae045
Narrative review of occupational exposures and noncommunicable diseases
Abstract
Objective: Within the scope of the Exposome Project for Health and Occupational Research on applying the exposome concept to working life health, we aimed to provide a broad overview of the status of knowledge on occupational exposures and associated health effects across multiple noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) to help inform research priorities.
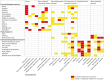
Methods: We conducted a narrative review of occupational risk factors that can be considered to have "consistent evidence for an association," or where there is "limited/inadequate evidence for an association" for 6 NCD groups: nonmalignant respiratory diseases; neurodegenerative diseases; cardiovascular/metabolic diseases; mental disorders; musculoskeletal diseases; and cancer. The assessment was done in expert sessions, primarily based on systematic reviews, supplemented with narrative reviews, reports, and original studies. Subsequently, knowledge gaps were identified, e.g. based on missing information on exposure-response relationships, gender differences, critical time-windows, interactions, and inadequate study quality.
Results: We identified over 200 occupational exposures with consistent or limited/inadequate evidence for associations with one or more of 60+ NCDs. Various exposures were identified as possible risk factors for multiple outcomes. Examples are diesel engine exhaust and cadmium, with consistent evidence for lung cancer, but limited/inadequate evidence for other cancer sites, respiratory, neurodegenerative, and cardiovascular diseases. Other examples are physically heavy work, shift work, and decision latitude/job control. For associations with limited/inadequate evidence, new studies are needed to confirm the association. For risk factors with consistent evidence, improvements in study design, exposure assessment, and case definition could lead to a better understanding of the association and help inform health-based threshold levels.
Conclusions: By providing an overview of knowledge gaps in the associations between occupational exposures and their health effects, our narrative review will help setting priorities in occupational health research. Future epidemiological studies should prioritize to include large sample sizes, assess exposures prior to disease onset, and quantify exposures. Potential sources of biases and confounding need to be identified and accounted for in both original studies and systematic reviews.
Keywords: aetiology; epidemiology; exposome; occupational health.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Occupational Hygiene Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
