PERFECTRA: a pragmatic, multicentre, real-life study comparing treat-to-target strategies with baricitinib versus TNF inhibitors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis after failure on csDMARDs
- PMID: 38816210
- PMCID: PMC11328659
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004291
PERFECTRA: a pragmatic, multicentre, real-life study comparing treat-to-target strategies with baricitinib versus TNF inhibitors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis after failure on csDMARDs
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of a strategy administering baricitinib versus one using TNF-inhibitors (TNFi) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) after conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) failure in a real-life treat-to-target (T2T) setting.
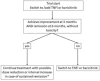
Methods: Patients with biological and targeted synthetic DMARD (b/tsDMARD) naïve RA with disease duration ≤5 years without contraindications to b/tsDMARD were randomised to either TNFi or baricitinib when csDMARD failed to achieve disease control in a T2T setting. Changes in clinical and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) were assessed at 12-week intervals for 48 weeks. The primary endpoint was non-inferiority, with testing for superiority if non-inferiority is demonstrated, of baricitinib strategy in the number of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology 50 (ACR50) response at 12 weeks. Secondary endpoints included 28-joint count Disease Activity Score with C reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) <2.6, changes in PROMs and radiographic progression.
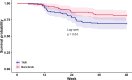
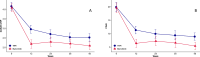
Results: A total of 199 patients (TNFi, n=102; baricitinib, n=97) were studied. Both study groups were similar. Baricitinib was both non-inferior and superior in achieving ACR50 response at week 12 (42% vs 20%). Moreover, 75% of baricitinib patients achieved DAS28-CRP <2.6 at week 12 compared with 46% of TNFi patients. On secondary outcomes throughout the duration of the study, the baricitinib strategy demonstrated comparable or better outcomes than TNFi strategy. Although not powered for safety, no unexpected safety signals were seen in this relatively small group of patients.
Conclusion: Up to present, in a T2T setting, patients with RA failing csDMARDs have two main strategies to consider, Janus Kinases inhibitor versus bDMARDs (in clinical practice, predominantly TNFi). The PERFECTRA study suggested that starting with baricitinib was superior over TNFi in achieving response at 12 weeks and resulted in improved outcomes across all studied clinical measures and PROMs throughout the study duration in these patients.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biological Therapy; Patient Reported Outcome Measures; Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CJvdL, MAHOV, PtK, DIT and MVdL report that the Investigator Initiated Study PERFECTRA was financially supported by an unrestricted grant by Eli Lilly. MVdL reports speaker fees by Eli Lilly and Galapagos. RB reports a research grant from Galapagos, advisory board payments from Janssen-Cilag bv, Galapagos, and Abbvie bv, payment for chairing an educational event from Janssen-Cilag bv.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
