Circ_RPPH1 facilitates progression of breast cancer via miR-1296-5p/TRIM14 axis
- PMID: 38816350
- PMCID: PMC11141472
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2360768
Circ_RPPH1 facilitates progression of breast cancer via miR-1296-5p/TRIM14 axis
Abstract
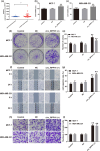
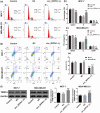
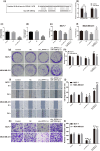
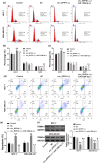
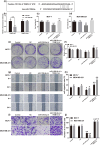
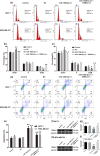
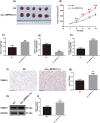
Circular RNA Ribonuclease P RNA Component H1 (circ_RPPH1) and microRNA (miRNA) miR-1296-5p play a crucial role in breast cancer (BC), but the molecular mechanism is vague. Evidence showed that miR-1296-5p can activate tripartite motif-containing 14 (TRIM14). Clinical indications of eighty BC patients were collected and the circ_RPPH1 expression was detected using real-time quantitative PCR. MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with overexpression or knockdown of circ_RPPH1, miR-1296-5p, or TRIM14. Cell counting kit-8, cell cloning formation, wound healing, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays were performed to investigate the malignant phenotype of BC. The dual-luciferase reporter gene analyses were applied to reveal the interaction between these target genes. Subcutaneous tumorigenic model mice were established with circ_RPPH1 overexpression MDA-MB-231 cells in vivo; the tumor weight and volume, levels of miR-1296-5 and TRIM14 mRNA were measured. Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to detect TRIM14 in cells and mice. Circ_RPPH1 levels were notably higher in BC patients and have been found to promote cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of BC cells. Circ_RPPH1 altered cell cycle and hindered apoptosis. Circ_RPPH1 knockdown or miR-1296-5p overexpression inhibited the malignant phenotype of BC. Furthermore, miR-1296-5p knockdown reversed circ_RPPH1's promotion effects on BC. Interestingly, TRIM14 overexpression counteracts the inhibitory effects of miR-1296-5p overexpression and circ_RPPH1 silencing on BC. Moreover, in BC tumor-bearing mice, circ_RPPH1 overexpression led to increased TRIM14 expression and facilitated tumor growth. Circ_RPPH1 enhanced BC progression through miR-1296-5p/TRIM14 axis, indicating its potential as a biomarker and therapeutic target in BC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; circular RNA ribonuclease P RNA component H1; microRNA-1296-5p; tripartite motif-containing 14.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circular RNA circ_0048764 promotes the development of breast cancer by regulating microRNA-1296-5p/tripartite motif containing 14 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):1963-1974. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1995990. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 34787066 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-RPPH1 knockdown retards breast cancer progression via miR-328-3p-mediated suppression of HMGA2.Clin Breast Cancer. 2022 Apr;22(3):e286-e295. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2021.08.009. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Clin Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34593318
-
circRNA RPPH1 Facilitates the Aggravation of Breast Cancer Development by Regulating miR-542-3p/ARHGAP1 Pathway.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2022 Oct;37(8):708-719. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.4381. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2022. PMID: 34402683
-
Circ_RPPH1 regulates glioma cell malignancy by binding to miR-627-5p/miR-663a to induce SDC1 expression.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Apr;37(4):1231-1245. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-00965-y. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35334040
-
Emerging discoveries on the role of TRIM14: from diseases to immune regulation.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Dec 24;10(1):513. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02276-w. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39719450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Engineering Circular RNA Vaccines.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 15;13(8):692. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080692. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role and clinical value of serum hsa_tsr011468 in lung adenocarcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Dec;30(6):226. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13350. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39364758 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0000515 sequesters microRNA-296-5p and elevates RNF44 expression to encourage the NSCLC progression.J Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 24;19(1):e70005. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.70005. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39995883 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Unveiling Their Roles and Exploring Therapeutic Potential.Biochem Genet. 2025 Apr;63(2):1219-1240. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11068-5. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 40029586 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
