Three-year outcomes of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19
- PMID: 38816608
- PMCID: PMC11186764
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02987-8
Three-year outcomes of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19
Abstract
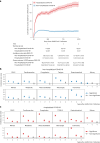
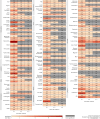
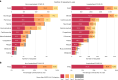
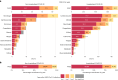
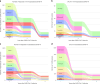
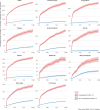
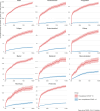
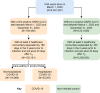
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection causes post-acute sequelae of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (PASC) in many organ systems. Risks of these sequelae have been characterized up to 2 years after infection, but longer-term follow-up is limited. Here we built a cohort of 135,161 people with SARS-CoV-2 infection and 5,206,835 controls from the US Department of Veterans Affairs who were followed for 3 years to estimate risks of death and PASC. Among non-hospitalized individuals, the increased risk of death was no longer present after the first year of infection, and risk of incident PASC declined over the 3 years but still contributed 9.6 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.4-18.7) disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 1,000 persons in the third year. Among hospitalized individuals, risk of death declined but remained significantly elevated in the third year after infection (incidence rate ratio: 1.29 (95% CI: 1.19-1.40)). Risk of incident PASC declined over the 3 years, but substantial residual risk remained in the third year, leading to 90.0 (95% CI: 55.2-124.8) DALYs per 1,000 persons. Altogether, our findings show reduction of risks over time, but the burden of mortality and health loss remains in the third year among hospitalized individuals.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Z.A.-A. reports receiving consultation fees from Gilead Sciences. Y.X. reports consulting for Guidepoint. Z.A.-A. and Y.X. report consulting (uncompensated) for Pfizer. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

