IL-27 maintains cytotoxic Ly6C+ γδ T cells that arise from immature precursors
- PMID: 38816652
- PMCID: PMC11251046
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00133-1
IL-27 maintains cytotoxic Ly6C+ γδ T cells that arise from immature precursors
Abstract
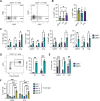
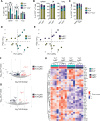
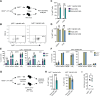
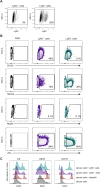
In mice, γδ-T lymphocytes that express the co-stimulatory molecule, CD27, are committed to the IFNγ-producing lineage during thymic development. In the periphery, these cells play a critical role in host defense and anti-tumor immunity. Unlike αβ-T cells that rely on MHC-presented peptides to drive their terminal differentiation, it is unclear whether MHC-unrestricted γδ-T cells undergo further functional maturation after exiting the thymus. Here, we provide evidence of phenotypic and functional diversity within peripheral IFNγ-producing γδ T cells. We found that CD27+ Ly6C- cells convert into CD27+Ly6C+ cells, and these CD27+Ly6C+ cells control cancer progression in mice, while the CD27+Ly6C- cells cannot. The gene signatures of these two subsets were highly analogous to human immature and mature γδ-T cells, indicative of conservation across species. We show that IL-27 supports the cytotoxic phenotype and function of mouse CD27+Ly6C+ cells and human Vδ2+ cells, while IL-27 is dispensable for mouse CD27+Ly6C- cell and human Vδ1+ cell functions. These data reveal increased complexity within IFNγ-producing γδ-T cells, comprising immature and terminally differentiated subsets, that offer new insights into unconventional T-cell biology.
Keywords: Cancer; Differentiation; IL-27; Innate; γδ T Cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Barros-Martins J, Schmolka N, Fontinha D, Pires de Miranda M, Simas JP, Brok I, Ferreira C, Veldhoen M, Silva-Santos B, Serre K. Effector γδ T cell differentiation relies on master but not auxiliary Th cell transcription factors. J Immunol. 2016;196:3642–3652. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501921. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beck BH, Kim HG, Kim H, Samuel S, Liu Z, Shrestha R, Haines H, Zinn K, Lopez RD. Adoptively transferred ex vivo expanded γδ T cells mediate in vivo antitumor activity in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;122:135–144. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0527-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019DecPhD1349/Breast Cancer Now (BCN)
- BB/R017808/1/UKRI | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- MR/V010972/1/UKRI | Medical Research Council (MRC)
- 217093/Z/19/Z/Wellcome Trust (WT)
- n/a/Annie McNab Bequest
- 2020 24/Little Princess Trust (LPT)
- 22706/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- S17-17/Tenovus (Tenovus Cancer Care)
- n/a/Stichting Sanquin Bloedvoorziening (Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation)
- C596/A25142,A31287,A29799,A29801,DRCPFA-Nov21\100001/Cancer Research UK (CRUK)
- 208990/Z/17/Z/Wellcome Trust (WT)
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

