Evolutionary origin and gradual accumulation with plant evolution of the LACS family
- PMID: 38816698
- PMCID: PMC11140897
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05194-2
Evolutionary origin and gradual accumulation with plant evolution of the LACS family
Abstract
Background: LACS (long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase) genes are widespread in organisms and have multiple functions in plants, especially in lipid metabolism. However, the origin and evolutionary dynamics of the LACS gene family remain largely unknown.
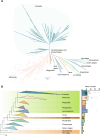
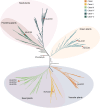
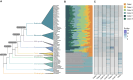
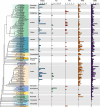
Results: Here, we identified 1785 LACS genes in the genomes of 166 diverse plant species and identified the clades (I, II, III, IV, V, VI) of six clades for the LACS gene family of green plants through phylogenetic analysis. Based on the evolutionary history of plant lineages, we found differences in the origins of different clades, with Clade IV originating from chlorophytes and representing the origin of LACS genes in green plants. The structural characteristics of different clades indicate that clade IV is relatively independent, while the relationships between clades (I, II, III) and clades (V, VI) are closer. Dispersed duplication (DSD) and transposed duplication (TRD) are the main forces driving the evolution of plant LACS genes. Network clustering analysis further grouped all LACS genes into six main clusters, with genes within each cluster showing significant co-linearity. Ka/Ks results suggest that LACS family genes underwent purifying selection during evolution. We analyzed the phylogenetic relationships and characteristics of six clades of the LACS gene family to explain the origin, evolutionary history, and phylogenetic relationships of different clades and proposed a hypothetical evolutionary model for the LACS family of genes in plants.
Conclusions: Our research provides genome-wide insights into the evolutionary history of the LACS gene family in green plants. These insights lay an important foundation for comprehensive functional characterization in future research.
Keywords: Evolutionary origin; LACS family; Phylogeny.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wang J, Li XX, Zhao XC, Na C, Liu HL, Miao HR, Zhou JH, Xiao JL, Zhao X, Han YP. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the abiotic-stress-responsive LACS gene family in soybean (Glycine max) Agronomy-Basel. 2022;12(7):18.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

