Global burden of pertussis in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
- PMID: 38816714
- PMCID: PMC11141049
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-18968-y
Global burden of pertussis in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to examine the impact of pertussis on the global, regional, and national levels between 1990 and 2019.
Methods: Data on pertussis on a global scale from 1990 to 2019 were collected from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. We performed a secondary analysis to report the global epidemiology and disease burden of pertussis.
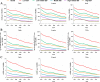
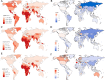
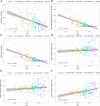
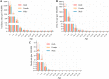
Results: During the period spanning from 1990 to 2019, pertussis exhibited a steady global decline in the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate (ASYR), and age-standardized death rate (ASDR). Nevertheless, upon delving into an in-depth analysis of various regions, it was apparent that ASIR in southern sub-Saharan Africa, ASYR and ASDR in high-income North America, and ASDR in Western Europe and Australasia, were witnessing an upward trajectory. Moreover, a negative correlation was observed between the Socio‑demographic Index (SDI) and burden inflicted by pertussis. Notably, the incidence of pertussis was comparatively lower in men than in women, with 0-4-year-olds emerging as the most profoundly affected demographic.
Conclusion: The global pertussis burden decreased from 1990 to 2019. However, certain regions and countries faced an increasing disease burden. Therefore, urgent measures are required to alleviate the pertussis burden in these areas.
Keywords: Burden; Epidemiology; GBD 2019; Global trend; Pertussis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global, regional and national trends in incidence and mortality of pertussis from 1990 to 2021 and the comparison before and during COVID-19: A modelling analysis.J Infect Public Health. 2025 Apr;18(4):102696. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2025.102696. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Infect Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39954608
-
Disease burden of AIDS in last 30-year period and its predicted level in next 25-years based on the global burden disease 2019.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):2384. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19934-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39223557 Free PMC article.
-
Global patterns of syphilis, gonococcal infection, typhoid fever, paratyphoid fever, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, and leprosy from 1990 to 2021: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Infect Dis Poverty. 2024 Sep 13;13(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s40249-024-01231-2. Infect Dis Poverty. 2024. PMID: 39267116 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of fracture of sternum and/or fracture of one or more ribs: a systematic analysis of incidence, YLDs with projections to 2030.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 3;13:1565478. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1565478. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40247872 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of uterine cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and 15-year projection: a systematic analysis and comparison with global levels.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01882-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39390595 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pertussis epidemiological surveillance and immunization history in children under five years in a megacity in China from 2019 to 2023.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2460273. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2460273. Epub 2025 Feb 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 39924641 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the timeliness of pertussis-containing vaccination: A cohort study in Shanghai, China.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2541496. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2541496. Epub 2025 Aug 1. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40747582 Free PMC article.
-
Post-COVID-19 pandemic changes in pertussis incidence among patients with acute respiratory tract infections in Zhejiang, China.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1448997. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1448997. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39184026 Free PMC article.
-
Pertussis in the Post-COVID-19 Era: Resurgence, Diagnosis, and Management.Infect Chemother. 2025 Mar;57(1):13-30. doi: 10.3947/ic.2024.0117. Infect Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40183651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pertussis Vaccination for Adults: An Updated Guide for Clinicians.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jan 11;13(1):60. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13010060. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2020 Release 1 Vaccine Coverage Collaborators Measuring routine childhood vaccination coverage in 204 countries and territories, 1980-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2020, Release 1. Lancet. 2021;398(10299):503–521. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00984-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Pertussis vaccines:WHO position paper-September 2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2015;90(35):433–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

