CircDCAF8 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-217/NAP1L1 Axis, and induces angiogenesis and regorafenib resistance via exosome-mediated transfer
- PMID: 38816735
- PMCID: PMC11137954
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05233-4
CircDCAF8 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-217/NAP1L1 Axis, and induces angiogenesis and regorafenib resistance via exosome-mediated transfer
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs), which are a new type of single-stranded circular RNA, have significant involvement in progression of many diseases, including tumors. Currently, multiple circRNAs have been identified in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Our study aims to investigate the function and mechanism of circDCAF8 in HCC.
Methods: The expression of circDCAF8 (hsa_circ_0014879) in HCC and para-carcinoma tissue samples was determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The biological function of circDCAF8 in HCC was confirmed by experiments conducted both in vitro and in vivo. And the relationship between circDCAF8, miR-217 and NAP1L1 was predicted by database and verified using qRT-PCR, RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation (RIP) and dual-luciferase reporter assays. Exosomes isolated from HCC cells were utilized to assess the connection of exosomal circDCAF8 with HCC angiogenesis and regorafenib resistance.
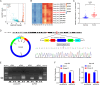
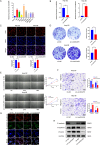
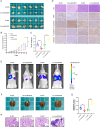
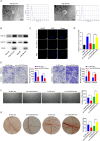
Results: CircDCAF8 is upregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines, and is linked to an unfavourable prognosis for HCC patients. Functionally, circDCAF8 was proved to facilitate proliferation, migration, invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transformation (EMT) in HCC cells. Animal examinations also validated the tumor-promoting characteristics of circDCAF8 on HCC. Besides, exosomal circDCAF8 promoted angiogenesis in HUVECs. Mechanistically, circDCAF8 interacted with miR-217 and NAP1L1 was a downstream protein of miR-217. CircDCAF8 promoted NAP1L1 expression by sponging miR-217. In addition, exosomes may transfer circDCAF8 from regorafenib-resistant HCC cells to sensitive cells, where it would confer a resistant phenotype.
Conclusion: CircDCAF8 facilitates HCC proliferation and metastasis via the miR-217/NAP1L1 axis. Meanwhile, circDCAF8 can promote angiogenesis and drive resistance to regorafenib, making it a viable therapeutic target for HCC patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 12;37(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0677-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 19;42(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02761-7. PMID: 29530052 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Hsa_circ_0003998 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-143-3p and PCBP1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 17;39(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01576-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32552766 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification of circular RNA circASH2L suppresses growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating hsa-miR-525-3p/MTUS2 axis.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):1026. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05745-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39543614 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-140-3p/KIF2A axis.Histol Histopathol. 2025 Aug;40(8):1239-1251. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-849. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Histol Histopathol. 2025. PMID: 39587911
-
CircUCK2(2,3) promotes cancer progression and enhances synergistic cytotoxicity of lenvatinib with EGFR inhibitors via activating CNIH4-TGFα-EGFR signaling.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 30;30(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00690-1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39885395 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD147-high extracellular vesicles promote gastric cancer metastasis via VEGF/AKT/eNOS and AKT/mTOR pathways.Oncogenesis. 2025 Jun 20;14(1):21. doi: 10.1038/s41389-025-00564-3. Oncogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40541935 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal circ_0001583 Drives Glioblastoma Cell Advancement Through the miR-647/CKAP2L Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10687-10706. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04875-9. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40229458 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Clinical Implications and Potential Strategies to Overcome the Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 25;16(23):3944. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233944. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs modulate cancer drug resistance: advances and challenges.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 28;8:17. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.195. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40201313 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the roles and molecular mechanisms of exosomal circular RNAs in regulating the pre-metastatic niche of tumors.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 19;16(1):568. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02374-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40252161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- VICENS Q. WESTHOF E Biogenesis Circular RNAs[J] Cell. 2014;159(1):13–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

