Differential gene expression and immune cell infiltration in maedi-visna virus-infected lung tissues
- PMID: 38816794
- PMCID: PMC11141007
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10448-2
Differential gene expression and immune cell infiltration in maedi-visna virus-infected lung tissues
Abstract
Background: Maedi-visna virus (MVV) is a lentivirus that infects monocyte/macrophage lineage cells in sheep, goats, and wild ruminants and causes pneumonia, mastitis, arthritis, and encephalitis. The immune response to MVV infection is complex, and a complete understanding of its infection and pathogenesis is lacking. This study investigated the in vivo transcriptomic patterns of lung tissues in sheep exposed to MVV using the RNA sequencing technology.
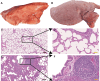
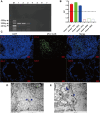
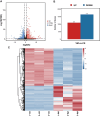
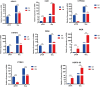
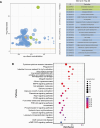
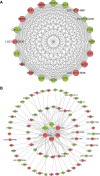
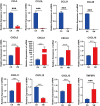
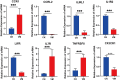
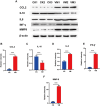
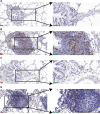
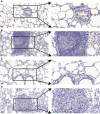
Result: The results indicated that 2,739 genes were significantly differentially expressed, with 1,643 downregulated genes and 1,096 upregulated genes. Many variables that could be unique to MVV infections were discovered. Gene Ontology analysis revealed that a significant proportion of genes was enriched in terms directly related to the immune system and biological responses to viral infections. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis revealed that the most enriched pathways were related to virus-host cell interactions and inflammatory responses. Numerous immune-related genes, including those encoding several cytokines and interferon regulatory factors, were identified in the protein-protein interaction network of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The expression of DEGs was evaluated using real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. CXCL13, CXCL6, CXCL11, CCR1, CXCL8, CXCL9, CXCL10, TNFSF8, TNFRSF8, IL7R, IFN-γ, CCL2, and MMP9 were upregulated. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to identify the types of immune cells that infiltrated MVV-infected tissues. B cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and macrophages were the most prevalent immune cells correlated with MVV infection in the lungs.
Conclusion: Overall, the findings of this study provide a comprehensive understanding of the in vivo host response to MVV infection and offer new perspectives on the gene regulatory networks that underlie pathogenesis in natural hosts.
Keywords: Differential expression; Immunopathogenesis; Maedi-Visna virus; Ovine progressive pneumonia; Pathogenesis; RNA-seq; Sheep.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maedi-visna virus and its relationship to human immunodeficiency virus.AIDS Rev. 2005 Oct-Dec;7(4):233-45. AIDS Rev. 2005. PMID: 16425963 Review.
-
Expression analysis of 13 ovine immune response candidate genes in Visna/Maedi disease progression.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Jul;36(4):405-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23582860
-
Detection and immune cell response of natural maedi visna virus (MVV) infection in Indian sheep and goats.Microb Pathog. 2022 Apr;165:105467. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105467. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35257804
-
Early events in immune evasion by the lentivirus maedi-visna occurring within infected lymphoid tissue.J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5187-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.67.9.5187-5197.1993. J Virol. 1993. PMID: 8394444 Free PMC article.
-
Maedi-visna virus infection in sheep: a review.Vet Res. 1998 May-Aug;29(3-4):341-67. Vet Res. 1998. PMID: 9689746 Review.
Cited by
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism-based analysis of linkage disequilibrium and runs of homozygosity patterns of indigenous sheep in the southern Taklamakan desert.BMC Genomics. 2025 Mar 18;26(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11445-9. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40102738 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immune Response Against Batai Virus, Bunyamwera Virus, and Their Reassortants.Viruses. 2024 Nov 26;16(12):1833. doi: 10.3390/v16121833. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39772143 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of concurrent infection with Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus and maedi-visna virus in China.J Vet Sci. 2024 Sep;25(5):e61. doi: 10.4142/jvs.24158. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39231786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pálsson PA. Maedi and Visna in sheep. Front Biology. 1976;44:17–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NDYB2022-6/High-level Talents Introduction to Scientific Research Start-up Project of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University
- 32072819/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021ZD0010/Science and Technology Major Special Project of Inner Mongolia
- 20151031/Grassland Talents Innovative Team Project of Inner Mongolia
- NMGIRT2412/the Innovation team project of Education Department of Inner Mongolia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

