Pre- and postpartum fear of childbirth and its predictors among rural women in China
- PMID: 38816809
- PMCID: PMC11138059
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-024-06585-x
Pre- and postpartum fear of childbirth and its predictors among rural women in China
Abstract
Background: Fear of childbirth (FOC) can influence both maternal and child health. Research on FOC in China is scarce, especially on rural women. This study aimed to assess pre- and postpartum FOC and its predictors among Chinese rural women.
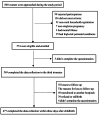
Methods: This was a prospective correlation study. A total of 569 women completed the prenatal questionnaire in the third trimester, and 477 of them completed the postpartum questionnaire within three days after childbirth. Maternal socio-demographic information, clinical information, childbirth self-efficacy and prenatal and postpartum FOC were investigated. FOC was evaluated using the Wijma Childbirth Expectancy/ Experience Questionnaire (WDEQ). Descriptive, bivariate, multivariate linear regression analysis, univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed.
Results: The mean pre- and postpartum FOC scores were 64.5 (standard deviation: 25.1) and 64.3 (standard deviation: 23.9), respectively, with 20.8% of women reporting severe fear before childbirth and 18.2% after childbirth. Multivariate linear regression analysis revealed predictors for higher levels of prenatal FOC including higher education level, nullipara, higher monthly household income, lower family support, and lower childbirth self-efficacy (p < 0.05) and the predictors for higher levels of postpartum FOC included unemployed status, lower childbirth self-efficacy, and higher prenatal FOC (p < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression showed that higher childbirth self-efficacy reduced the likelihood of severe prenatal FOC (OR: 0.99, p < 0.001), while severe prenatal FOC increased the likelihood of severe postpartum FOC (OR: 3.57, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The rural women have high levels of FOC before and after childbirth, with approximately 20% experiencing severe FOC during both periods. Higher education level, nullipara, higher monthly household income, lower family support, and lower childbirth self-efficacy are predictors of heightened prenatal FOC. Unemployed status, lower childbirth self-efficacy, and higher prenatal FOC are predictors of heightened postpartum FOC. Notably, enhancing childbirth self-efficacy emerges as crucial in mitigating severe prenatal FOC, while severe prenatal FOC significantly increases the likelihood of severe postpartum FOC. The development of targeted intervention strategies for the above factors can help reduce women's FOC level and improve their overall pregnancy and childbirth experience.
Keywords: Childbirth; Fear; Postpartum; Prenatal; Rural women.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical