CGRP as a potential mediator for the sexually dimorphic responses to traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 38816868
- PMCID: PMC11138127
- DOI: 10.1186/s13293-024-00619-x
CGRP as a potential mediator for the sexually dimorphic responses to traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: The outcomes of traumatic brain injury (TBI) exhibit variance contingent upon biological sex. Although female sex hormones exert neuroprotective effects, the administration of estrogen and progesterone has not yielded conclusive results. Hence, it is conceivable that additional mediators, distinct from female sex hormones, merit consideration due to their potential differential impact on TBI outcomes. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) exhibits sexually dimorphic expression and demonstrates neuroprotective effects in acute brain injuries. In this study, we aimed to examine sex-based variations in TBI structural and functional outcomes with respect to CGRP expression.
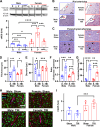
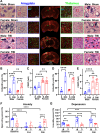
Methods: Male and female Sprague Dawley rats were exposed to controlled cortical impact to induce severe TBI, followed by interventions with and without CGRP inhibition. In the acute phase of TBI, the study centered on elucidating the influence of CGRP on oxidative stress, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) signaling in the peri-impact tissue. Subsequently, during the chronic phase of TBI, the investigation expanded to evaluate CGRP expression in relation to lesion volume, microvascular dysfunction, and white matter injury, as well as working and spatial memory, anxiety-like, and depression-like behaviors in subjects of both sexes.
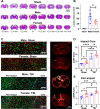
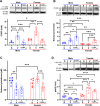
Results: Female rats exhibited elevated levels of CGRP in the peri-impact brain tissue during both baseline conditions and in the acute and chronic phases of TBI, in comparison to age-matched male counterparts. Enhanced CGRP levels in specific brain sub-regions among female rats correlated with superior structural and functional outcomes following TBI compared to their male counterparts. CGRP inhibition induced heightened oxidative stress and a reduction in the expression of Nrf2 and eNOS in both male and female rats, with the observed alteration being more pronounced in females than in males.
Conclusions: This study marks the inaugural identification of CGRP as a downstream mediator contributing to the sexually dimorphic response observed in TBI outcomes.
Keywords: Anxiety; Calcitonin gene-related peptide; Depression; Memory; Microvascular dysfunction; Oxidative stress; Sex hormones; Sexual dimorphism; Traumatic brain injury.
Plain language summary
Investigating sex disparities in traumatic brain injury (TBI) is crucial for the advancement of precision therapeutics. Despite the neuroprotective effects demonstrated by female sex hormones, the administration of estrogen and progesterone has not produced conclusive results. Therefore, it is conceivable that additional mediators, separate from female sex hormones, warrant consideration due to their potential differential influence on TBI outcomes. In this study, we examined sex-related variations in calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) expression in peri-impact brain tissue and investigated its potential implications on associated TBI outcomes. CGRP exhibits sexually dimorphic expression and exerts a multifaceted influence on diverse physiological processes that contribute to the pathophysiology of TBI. Our findings reveal that female rats exhibit heightened CGRP levels at both baseline and post-TBI within specific brain sub-regions, thereby contributing to superior structural and functional outcomes compared to their age-matched male counterparts. Additionally, we identified substantial sex-based variations in mechanisms modulated by CGRP pertaining to oxidative stress and microvascular dysfunction. The disparities in CGRP levels may be crucial for comprehending the advantageous outcomes noted in female TBI. Therefore, elucidating the sex-related distinctions in CGRP within TBI brains could pave the way for improved management and treatment strategies for TBI in both male and female individuals.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no biomedical financial interests or potential competing interests to report.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhanced post-traumatic headache-like behaviors and diminished contribution of peripheral CGRP in female rats following a mild closed head injury.Cephalalgia. 2020 Jun;40(7):748-760. doi: 10.1177/0333102420907597. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Cephalalgia. 2020. PMID: 32077327 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in effectiveness of CGRP receptor antagonism for treatment of acute and persistent headache-like pain in a mouse model of mild traumatic brain injury.Cephalalgia. 2025 Feb;45(2):3331024251321087. doi: 10.1177/03331024251321087. Cephalalgia. 2025. PMID: 39980371
-
Hydrogen-rich water attenuates oxidative stress in rats with traumatic brain injury via Nrf2 pathway.J Surg Res. 2018 Aug;228:238-246. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.03.024. Epub 2018 Apr 11. J Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29907217
-
Bimodal functions of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the brain.Life Sci. 2024 Dec 15;359:123177. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123177. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39486618 Review.
-
Evaluation of outcomes of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-targeting therapies for acute and preventive migraine treatment based on patient sex.Cephalalgia. 2024 Mar;44(3):3331024241238153. doi: 10.1177/03331024241238153. Cephalalgia. 2024. PMID: 38477313 Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-repair macrophages driven by CGRP rescue white matter integrity following intracerebral hemorrhage.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jun 21;22(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03483-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40544251 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological Mechanisms Underlying Psychological Dysfunction After Brain Injuries.Cells. 2025 Jan 8;14(2):74. doi: 10.3390/cells14020074. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

